WikiPathways: connecting communities
- PMID: 33211851
- PMCID: PMC7779061
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1024
WikiPathways: connecting communities
Abstract
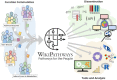
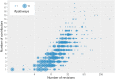
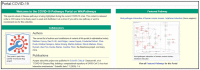
WikiPathways (https://www.wikipathways.org) is a biological pathway database known for its collaborative nature and open science approaches. With the core idea of the scientific community developing and curating biological knowledge in pathway models, WikiPathways lowers all barriers for accessing and using its content. Increasingly more content creators, initiatives, projects and tools have started using WikiPathways. Central in this growth and increased use of WikiPathways are the various communities that focus on particular subsets of molecular pathways such as for rare diseases and lipid metabolism. Knowledge from published pathway figures helps prioritize pathway development, using optical character and named entity recognition. We show the growth of WikiPathways over the last three years, highlight the new communities and collaborations of pathway authors and curators, and describe various technologies to connect to external resources and initiatives. The road toward a sustainable, community-driven pathway database goes through integration with other resources such as Wikidata and allowing more use, curation and redistribution of WikiPathways content.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

