RiboDiPA: a novel tool for differential pattern analysis in Ribo-seq data
- PMID: 33211868
- PMCID: PMC7708064
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1049
RiboDiPA: a novel tool for differential pattern analysis in Ribo-seq data
Abstract
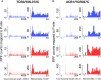
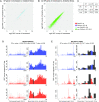
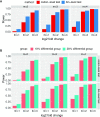
Ribosome profiling, also known as Ribo-seq, has become a popular approach to investigate regulatory mechanisms of translation in a wide variety of biological contexts. Ribo-seq not only provides a measurement of translation efficiency based on the relative abundance of ribosomes bound to transcripts, but also has the capacity to reveal dynamic and local regulation at different stages of translation based on positional information of footprints across individual transcripts. While many computational tools exist for the analysis of Ribo-seq data, no method is currently available for rigorous testing of the pattern differences in ribosome footprints. In this work, we develop a novel approach together with an R package, RiboDiPA, for Differential Pattern Analysis of Ribo-seq data. RiboDiPA allows for quick identification of genes with statistically significant differences in ribosome occupancy patterns for model organisms ranging from yeast to mammals. We show that differential pattern analysis reveals information that is distinct and complimentary to existing methods that focus on translational efficiency analysis. Using both simulated Ribo-seq footprint data and three benchmark data sets, we illustrate that RiboDiPA can uncover meaningful pattern differences across multiple biological conditions on a global scale, and pinpoint characteristic ribosome occupancy patterns at single codon resolution.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

