Oxidative Stress and Preeclampsia-Associated Prothrombotic State
- PMID: 33212799
- PMCID: PMC7696949
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9111139
Oxidative Stress and Preeclampsia-Associated Prothrombotic State
Abstract
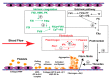
Preeclampsia (PE) is a common obstetric disease characterized by hypertension, proteinuria, and multi-system dysfunction. It endangers both maternal and fetal health. Although hemostasis is critical for preventing bleeding complications during pregnancy, delivery, and post-partum, PE patients often develop a severe prothrombotic state, potentially resulting in life-threatening thrombosis and thromboembolism. The cause of this thrombotic complication is multi-factorial, involving endothelial cells, platelets, adhesive ligands, coagulation, and fibrinolysis. Increasing evidence has shown that hemostatic cells and factors undergo oxidative modifications during the systemic inflammation found in PE patients. However, it is largely unknown how these oxidative modifications of hemostasis contribute to development of the PE-associated prothrombotic state. This knowledge gap has significantly hindered the development of predictive markers, preventive measures, and therapeutic agents to protect women during pregnancy. Here we summarize reports in the literature regarding the effects of oxidative stress and antioxidants on systemic hemostasis, with emphasis on the condition of PE.
Keywords: coagulation; hemostasis; oxidative stress; platelets; preeclampsia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prothrombotic state associated with preeclampsia.Curr Opin Hematol. 2021 Sep 1;28(5):323-330. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000678. Curr Opin Hematol. 2021. PMID: 34267080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radicals, Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress and Preeclampsia.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2019;19(3):178-193. doi: 10.2174/1389557518666181015151350. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30324879 Review.
-
Pathological haemostasis and "prothrombotic state" in Behçet's disease.Thromb Res. 2002 Jan 15;105(2):125-33. doi: 10.1016/s0049-3848(02)00006-3. Thromb Res. 2002. PMID: 11958802 Review.
-
Syncytiotrophoblast-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Pathophysiology of Preeclampsia.Front Physiol. 2019 Oct 1;10:1236. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01236. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31632289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI) contribute to impairment of fibrinolysis in patients with preeclampsia and/or intrauterine fetal growth retardation?Thromb Haemost. 2002 Oct;88(4):644-7. Thromb Haemost. 2002. PMID: 12362237
Cited by
-
Thrombin in Pregnancy and Preeclampsia: Expression, Localization, and Vasoactivity in Brain and Microvessels From Rats.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 1;84(2):250-260. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001579. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38922586 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Oxidative Stress of Environmental Origin on the Onset of Placental Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 1;11(1):106. doi: 10.3390/antiox11010106. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between perinatal complications and venous thromboembolism in postpartum women.J Glob Health. 2025 May 16;15:04153. doi: 10.7189/jogh.15.04153. J Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40375726 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic theory of preeclampsia: implications for maternal cardiovascular health.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024 Sep 1;327(3):H582-H597. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00170.2024. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38968164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular Oxidative Stress.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Mar 6;10(3):399. doi: 10.3390/antiox10030399. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33800761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellamy L., Casas J.P., Hingorani A.D., Williams D.J. Pre-eclampsia and risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer in later life: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2007;335:974. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39335.385301.BE. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

