Clinical Utility of the Pathogenesis-Related Proteins in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 33212853
- PMCID: PMC7698353
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21228661
Clinical Utility of the Pathogenesis-Related Proteins in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
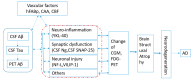
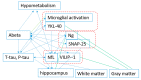
Research on the Aβ cascade and alternations of biomarkers in neuro-inflammation, synaptic dysfunction, and neuronal injury followed by Aβ have progressed. But the question is how to use the biomarkers. Here, we examine the evidence and pathogenic implications of protein interactions and the time order of alternation. After the deposition of Aβ, the change of tau, neurofilament light chain (NFL), and neurogranin (Ng) is the main alternation and connection to others. Neuro-inflammation, synaptic dysfunction, and neuronal injury function is exhibited prior to the structural and metabolic changes in the brain following Aβ deposition. The time order of such biomarkers compared to the tau protein is not clear. Despite the close relationship between biomarkers and plaque Aβ deposition, several factors favor one or the other. There is an interaction between some proteins that can predict the brain amyloid burden. The Aβ cascade hypothesis could be the pathway, but not all subjects suffer from Alzheimer's disease (AD) within a long follow-up, even with very elevated Aβ. The interaction of biomarkers and the time order of change require further research to identify the right subjects and right molecular target for precision medicine therapies.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; biomarkers dynamics; interaction; time order.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association between cerebrospinal fluid and plasma neurodegeneration biomarkers with brain atrophy in Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Aging. 2017 Oct;58:14-29. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jun 17. Neurobiol Aging. 2017. PMID: 28692877
-
Cerebrospinal fluid tau, neurogranin, and neurofilament light in Alzheimer's disease.EMBO Mol Med. 2016 Oct 4;8(10):1184-1196. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201606540. Print 2016 Oct. EMBO Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27534871 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of neurodegeneration, synaptic integrity, and astroglial activation across the clinical Alzheimer's disease spectrum.Alzheimers Dement. 2019 May;15(5):644-654. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Alzheimers Dement. 2019. PMID: 30853464
-
Key Peptides and Proteins in Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019;20(6):577-599. doi: 10.2174/1389203720666190103123434. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2019. PMID: 30605056 Review.
-
Beta-amyloid sequelae in the eye: a critical review on its diagnostic significance and clinical relevance in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Psychiatry. 2017 Mar;22(3):353-363. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.251. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Mol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28093567 Review.
Cited by
-
Salidroside Ameliorates Alzheimer's Disease by Targeting NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Pyroptosis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jan 21;13:809433. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.809433. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35126093 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review of amyloid-beta clearance proteins from the brain to the periphery: implications for Alzheimer's disease diagnosis and therapeutic targets.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Dec 1;20(12):3574-3590. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00865. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 39820231 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of colony stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R) as a potential therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative diseases: opportunities and challenges.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Apr 2;79(4):219. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04225-1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35366105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects on Autophagy of Moxibustion at Governor Vessel Acupoints in APP/PS1double-Transgenic Alzheimer's Disease Mice through the lncRNA Six3os1/miR-511-3p/AKT3 Molecular Axis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Oct 5;2022:3881962. doi: 10.1155/2022/3881962. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36248429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Timmers M., Streffer J.R., Russu A., Tominaga Y., Shimizu H. Pharmacodynamics of atabecestat (JNJ-54861911), an oral BACE1 inhibitor in patients with early Alzheimer’s disease: Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Alzheimers Res. 2018;10:85. doi: 10.1186/s13195-018-0415-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

