Aeromonas hydrophila RIT668 and Citrobacter portucalensis RIT669-Potential Zoonotic Pathogens Isolated from Spotted Turtles
- PMID: 33212916
- PMCID: PMC7698337
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8111805
Aeromonas hydrophila RIT668 and Citrobacter portucalensis RIT669-Potential Zoonotic Pathogens Isolated from Spotted Turtles
Abstract
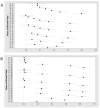
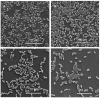
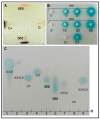
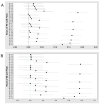
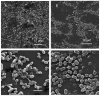
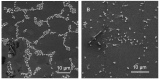
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the biggest challenges of the 21st century, and biofilm formation enables bacteria to resist antibiotic at much higher concentrations than planktonic cells. Earlier, we showed that the Gram-negative Aeromonas hydrophila RIT668 and Citrobacter portucalensis RIT669 (closely related to C. freundii NBRC 12681) from infected spotted turtles (Clemmys guttata), formed biofilms and upregulated toxin expression on plastic surfaces, and were predicted to possess multiple antibiotic resistance genes. Here, we show that they each resist several antibiotics in the planktonic phase, but were susceptible to neomycin, and high concentrations of tetracycline and cotrimoxazole. The susceptibility of their biofilms to neomycin and cotrimoxazole was tested using the Calgary device. For A. hydrophila, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) = 500-1000, and the minimum biofilm eradication concentration (MBEC) > 1000 μg/mL, using cotrimoxazole, and MIC = 32.3-62.5, and MBEC > 1000 μg/mL, using neomycin. For C. freundii MIC = 7.8-15.6, and, MBEC > 1000 μg/mL, using cotrimoxazole, and MIC = 7.8, and MBEC > 1000 μg/mL, using neomycin. Both A. hydrophila and C. portucalensis activated an acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) dependent biosensor, suggesting that quorum sensing could mediate biofilm formation. Their multidrug resistance in the planktonic form, and weak biofilm eradication even with neomycin and cotrimoxazole, indicate that A. hydrophila and C. portucalensis are potential zoonotic pathogens, with risks for patients living with implants.
Keywords: Aeromonas hydrophila; Citrobacter portucalensis; antibiotics; antibiotics resistance; quorum sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

