The Sleeping Brain: Harnessing the Power of the Glymphatic System through Lifestyle Choices
- PMID: 33212927
- PMCID: PMC7698404
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci10110868
The Sleeping Brain: Harnessing the Power of the Glymphatic System through Lifestyle Choices
Abstract
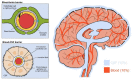
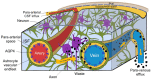
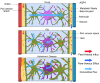
The glymphatic system is a "pseudo-lymphatic" perivascular network distributed throughout the brain, responsible for replenishing as well as cleansing the brain. Glymphatic clearance is the macroscopic process of convective fluid transport in which harmful interstitial metabolic waste products are removed from the brain intima. This paper addresses the glymphatic system, its dysfunction and the major consequences of impaired clearance in order to link neurodegeneration and glymphatic activity with lifestyle choices. Glymphatic clearance can be manipulated by sleep deprivation, cisterna magna puncture, acetazolamide or genetic deletion of AQP4 channels, but how lifestyle choices affect this brain-wide clearance system remains to be resolved. This paper will synthesize existing literature on glymphatic clearance, sleep, Alzheimer's disease and lifestyle choices, in order to harness the power of this mass transport system, promote healthy brain ageing and possibly prevent neurodegenerative processes. This paper concludes that 1. glymphatic clearance plays a major role in Alzheimer's pathology; 2. the vast majority of waste clearance occurs during sleep; 3. dementias are associated with sleep disruption, alongside an age-related decline in AQP4 polarization; and 4. lifestyle choices such as sleep position, alcohol intake, exercise, omega-3 consumption, intermittent fasting and chronic stress all modulate glymphatic clearance. Lifestyle choices could therefore alter Alzheimer's disease risk through improved glymphatic clearance, and could be used as a preventative lifestyle intervention for both healthy brain ageing and Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; amyloid-beta; disease prevention; glymphatic system; protein aggregates; sleep.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

