Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms
- PMID: 33212950
- PMCID: PMC7698413
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21228671
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms
Abstract
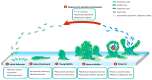
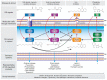
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic human pathogen causing devastating acute and chronic infections in individuals with compromised immune systems. Its highly notorious persistence in clinical settings is attributed to its ability to form antibiotic-resistant biofilms. Biofilm is an architecture built mostly by autogenic extracellular polymeric substances which function as a scaffold to encase the bacteria together on surfaces, and to protect them from environmental stresses, impedes phagocytosis and thereby conferring the capacity for colonization and long-term persistence. Here we review the current knowledge on P. aeruginosa biofilms, its development stages, and molecular mechanisms of invasion and persistence conferred by biofilms. Explosive cell lysis within bacterial biofilm to produce essential communal materials, and interspecies biofilms of P. aeruginosa and commensal Streptococcus which impedes P. aeruginosa virulence and possibly improves disease conditions will also be discussed. Recent research on diagnostics of P. aeruginosa infections will be investigated. Finally, therapeutic strategies for the treatment of P. aeruginosa biofilms along with their advantages and limitations will be compiled.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; biofilms; quorum sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Wu W., Jin Y., Bai F., Jin S. Chapter 41—Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. In: Tang Y.-W., Sussman M., Liu D., Poxton I., Schwartzman J., editors. Molecular Medical Microbiology. 2nd ed. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2015. pp. 753–767. - DOI
-
- Gomila A., Carratalà J., Badia J.M., Camprubí D., Piriz M., Shaw E., Diaz-Brito V., Espejo E., Nicolás C., Brugués M., et al. Preoperative oral antibiotic prophylaxis reduces Pseudomonas aeruginosa surgical site infections after elective colorectal surgery: A multicenter prospective cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018;18:507. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3413-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Prioritization of Pathogens to Guide Discovery, Research and Development of New Antibiotics for Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections, Including Tuberculosis. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

