The Kubic FLOTAC microscope (KFM): a new compact digital microscope for helminth egg counts
- PMID: 33213534
- PMCID: PMC7938342
- DOI: 10.1017/S003118202000219X
The Kubic FLOTAC microscope (KFM): a new compact digital microscope for helminth egg counts
Abstract
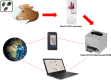
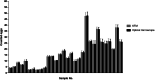
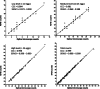
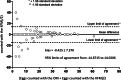
The Kubic FLOTAC microscope (KFM) is a compact, low-cost, versatile and portable digital microscope designed to analyse fecal specimens prepared with Mini-FLOTAC or FLOTAC, in both field and laboratory settings. In this paper, we present the characteristics of the KFM along with its first validation for fecal egg count (FEC) of gastrointestinal nematodes (GINs) in cattle. For this latter purpose, a study was performed on 30 fecal samples from cattle experimentally infected by GINs to compare the performance of Mini-FLOTAC either using a traditional optical microscope (OM) or the KFM. The results of the comparison showed a substantial agreement (concordance correlation coefficient = 0.999), with a very low discrepancy (−0.425 ± 7.370) between the two microscopes. Moreover, the KFM captured images comparable with the view provided by the traditional OM. Therefore, the combination of sensitive, accurate, precise and standardized FEC techniques, as the Mini-FLOTAC, with a reliable automated system, will permit the real-time observation and quantification of parasitic structures, thanks also to artificial intelligence software, that is under development. For these reasons, the KFM is a promising tool for an accurate and efficient FEC to improve parasite diagnosis and to assist new generations of operators in veterinary and public health.
Keywords: Digital microscope; Kubic FLOTAC microscope; Mini-FLOTAC; Tele-Parasitology; fecal egg count.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cattle gastrointestinal nematode egg-spiked faecal samples: high recovery rates using the Mini-FLOTAC technique.Parasit Vectors. 2020 May 6;13(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04107-0. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32375871 Free PMC article.
-
The comparison of FLOTAC, FECPAK and McMaster techniques for nematode egg counts in cattle.Acta Parasitol. 2014 Oct;59(4):625-8. doi: 10.2478/s11686-014-0282-7. Epub 2014 Sep 20. Acta Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 25236271
-
Comparison of fecal egg counting methods in four livestock species.Vet Parasitol. 2018 Jun 15;257:21-27. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2018.05.015. Epub 2018 May 26. Vet Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 29907188
-
Rapid assessment of faecal egg count and faecal egg count reduction through composite sampling in cattle.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Jul 16;12(1):353. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3601-x. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31311591 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal nematode parasites of grazing ruminants: a comprehensive literature review of diagnostic methods for quantifying parasitism, larval differentiation and measuring anthelmintic resistance.N Z Vet J. 2025 May;73(3):149-164. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2024.2415029. Epub 2024 Nov 10. N Z Vet J. 2025. PMID: 39522537 Review.
Cited by
-
Schistosomiasis diagnosis: Challenges and opportunities for elimination.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Jul 11;18(7):e0012282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012282. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38990839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimating the Prevalence and Factors Affecting the Shedding of Helminth Eggs in Irish Equine Populations.Animals (Basel). 2023 Feb 7;13(4):581. doi: 10.3390/ani13040581. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830368 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of FECPAKG2, a modified Mini-FLOTAC technique and combined sedimentation and flotation for the coproscopic examination of helminth eggs in horses.Parasit Vectors. 2022 May 12;15(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05266-y. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 35549990 Free PMC article.
-
Automating parasite egg detection: insights from the first AI-KFM challenge.Front Artif Intell. 2024 Aug 29;7:1325219. doi: 10.3389/frai.2024.1325219. eCollection 2024. Front Artif Intell. 2024. PMID: 39268195 Free PMC article.
-
Relative egg extraction efficiencies of manual and automated fecal egg count methods in equines.Helminthologia. 2024 Apr 23;61(1):20-29. doi: 10.2478/helm-2024-0007. eCollection 2024 Mar. Helminthologia. 2024. PMID: 38659463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cain JL, Slusarewicz P, Rutledge MH, McVey MR, Wielgus KM, Zynda KM, Wehling LM, Scare JA, Steuer AE and Nielsen MK (2020) Diagnostic performance of McMaster, Wisconsin, and automated egg counting techniques for enumeration of equine strongyle eggs in fecal samples. Veterinary Parasitology 284, 109–117. - PubMed
-
- Cools P, Vlaminck J, Albonico M, Ame S, Ayana M, José Antonio BP, Cringoli G, Dana D, Keiser J, Maurelli MP, Maya C, Matoso LF, Montresor A, Mekonnen Z, Mirams G, Corrêa-Oliveira R, Pinto SA, Rinaldi L, Sayasone S, Thomas E, Verweij JJ, Vercruysse J and Levecke B (2019) Diagnostic performance of a single and duplicate Kato-Katz, Mini-FLOTAC, FECPAKG2 and qPCR for the detection and quantification of soil-transmitted helminths in three endemic countries. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 13, e0007446. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cringoli G, Rinaldi L, Maurelli MP and Utzinger J (2010) FLOTAC: new multivalent techniques for qualitative and quantitative copromicroscopic diagnosis of parasites in animals and humans. Nature Protocols 5, 503–515. - PubMed
-
- Cringoli G, Maurelli MP, Levecke B, Bosco A, Vercruysse J, Utzinger J and Rinaldi L (2017) The Mini-FLOTAC technique for the diagnosis of helminth and protozoan infections in humans and animals. Nature Protocols 12, 1723–1732. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

