The impact of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) response on central-line-associated bloodstream infections and blood culture contamination rates at a tertiary-care center in the Greater Detroit area
- PMID: 33213553
- PMCID: PMC8185425
- DOI: 10.1017/ice.2020.1335
The impact of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) response on central-line-associated bloodstream infections and blood culture contamination rates at a tertiary-care center in the Greater Detroit area
Abstract
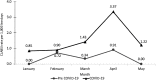
We conducted a comparative retrospective study to quantify the impact of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) on patient safety. We found a statistically significant increase in central-line-associated bloodstream infections and blood culture contamination rates during the pandemic. Increased length of stay and mortality were also observed during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Figures
References
-
- Haddadin Y, Annamaraju P, Regunath H. Central-line–associated blood stream infections (CLABSIs). NCBI Resources website. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430891/. Published 2020. Accessed July 25, 2020, 2020.
-
- Adalja AA, Toner E, Inglesby TV. Priorities for the US health community responding to COVID-19. JAMA 2020;323:1343–1344. - PubMed
-
- National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Patient Safety Component Manual. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/pdfs/pscmanual/pcsmanual_current.pdf. Published 2020. Accessed September 15, 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

