Autochthonous West Nile virus infection outbreak in humans, Leipzig, Germany, August to September 2020
- PMID: 33213686
- PMCID: PMC7678033
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.46.2001786
Autochthonous West Nile virus infection outbreak in humans, Leipzig, Germany, August to September 2020
Abstract
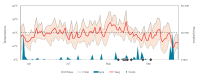
Following a distinct summer heat wave, nine autochthonous cases of West Nile fever and West Nile neuroinvasive disease, including one fatality, were observed in Leipzig, Germany, in August and September 2020. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated close relationships in viruses from humans, animals and mosquitos in eastern Germany, obtained during the preceding 2 years. The described large cluster of autochthonous West Nile virus infections in Germany indicates endemic seasonal circulation of lineage 2 viruses in the area.
Keywords: Outbreak; Viral encephalitis; West Nile fever; West Nile neuroinvasive disease; arboviruses; zoonoses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- European Commission. European Commission implementing decision of 8 August 2012 amending Decision 2002/253/EC laying down case definitions for reporting communicable diseases to the Community network under Decision No 2119/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. 27.9.2012:L 262. Official Journal of the European Union. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union. 27 Sep 2012. Available from: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2012:262:0001...
-
- Eiden M, Vina-Rodriguez A, Hoffmann B, Ziegler U, Groschup MH. Two new real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays with unique target sites for the specific and sensitive detection of lineages 1 and 2 West Nile virus strains. Journal of veterinary diagnostic investigation: official publication of the American Association of Veterinary Laboratory Diagnosticians. Inc. 2010;22(5):748-53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases