Sources of Metacognitive Inefficiency
- PMID: 33214066
- PMCID: PMC8610081
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tics.2020.10.007
Sources of Metacognitive Inefficiency
Abstract
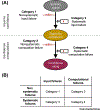
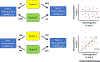
Confidence judgments are typically less informative about one's accuracy than they could be; a phenomenon we call metacognitive inefficiency. We review the existence of different sources of metacognitive inefficiency and classify them into four categories based on whether the corruption is due to: (i) systematic or nonsystematic influences, and (ii) the input to or the computation of the metacognitive system. Critically, the existence of different sources of metacognitive inefficiency provides an alternative explanation for behavioral findings typically interpreted as evidence for domain-specific (and against domain-general) metacognitive systems. We argue that, contrary to the dominant assumption in the field, metacognitive failures are not monolithic and suggest that understanding the sources of metacognitive inefficiency should be a primary goal of the science of metacognition.
Keywords: confidence; metacognition; metacognitive inefficiency; metacognitive noise; perceptual decision making.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Metcalfe J and Shimamura AP (1994) Metacognition: knowing about knowing, MIT Press.
-
- Baranski JV and Petrusic WM (1994) The calibration and resolution of confidence in perceptual judgments. Percept. Psychophys. 55, 412–428 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

