Large-scale analysis of iliopsoas muscle volumes in the UK Biobank
- PMID: 33214629
- PMCID: PMC7677387
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-77351-0
Large-scale analysis of iliopsoas muscle volumes in the UK Biobank
Abstract
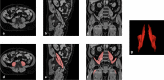
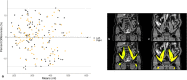
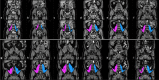
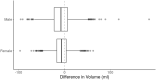
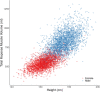
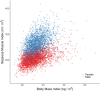
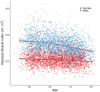
Psoas muscle measurements are frequently used as markers of sarcopenia and predictors of health. Manually measured cross-sectional areas are most commonly used, but there is a lack of consistency regarding the position of the measurement and manual annotations are not practical for large population studies. We have developed a fully automated method to measure iliopsoas muscle volume (comprised of the psoas and iliacus muscles) using a convolutional neural network. Magnetic resonance images were obtained from the UK Biobank for 5000 participants, balanced for age, gender and BMI. Ninety manual annotations were available for model training and validation. The model showed excellent performance against out-of-sample data (average dice score coefficient of 0.9046 ± 0.0058 for six-fold cross-validation). Iliopsoas muscle volumes were successfully measured in all 5000 participants. Iliopsoas volume was greater in male compared with female subjects. There was a small but significant asymmetry between left and right iliopsoas muscle volumes. We also found that iliopsoas volume was significantly related to height, BMI and age, and that there was an acceleration in muscle volume decrease in men with age. Our method provides a robust technique for measuring iliopsoas muscle volume that can be applied to large cohorts.
Conflict of interest statement
MC and YL are employees of Calico Life Sciences LLC. NB, JAF, JDB, ELT and BW declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CT imaging-derived phenotypes for abdominal muscle and their association with age and sex in a medical biobank.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 26;14(1):14807. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64603-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38926479 Free PMC article.
-
The peri-articular muscle envelope of the hip (PAME) shows atrophy in patients with refractory groin pain after iliopsoas tenotomy.Hip Int. 2025 Mar;35(2):190-197. doi: 10.1177/11207000241309600. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Hip Int. 2025. PMID: 39760249
-
Development and validation of a reliable method for automated measurements of psoas muscle volume in CT scans using deep learning-based segmentation: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2024 May 22;14(5):e079417. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-079417. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38777592 Free PMC article.
-
Iliopsoas compartment: normal anatomy and pathologic processes.Radiographics. 1995 Nov;15(6):1285-97. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.15.6.8577956. Radiographics. 1995. PMID: 8577956 Review.
-
Anatomy, pathology, imaging and intervention of the iliopsoas muscle revisited.Emerg Radiol. 2008 Sep;15(5):295-310. doi: 10.1007/s10140-008-0703-8. Epub 2008 Jun 12. Emerg Radiol. 2008. PMID: 18548299 Review.
Cited by
-
Pretransplant Psoas Muscle Cross-Sectional Area and Postkidney Transplant Outcomes.Transplant Proc. 2022 Sep;54(7):1816-1821. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2022.05.035. Epub 2022 Aug 4. Transplant Proc. 2022. PMID: 35933230 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of sarcopenia on the postoperative outcome in colorectal cancer surgery.Med Pharm Rep. 2023 Jan;96(1):20-27. doi: 10.15386/mpr-2483. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Med Pharm Rep. 2023. PMID: 36818326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of a Fully Automatic Deep Learning-Based Method for the Measurement of Psoas Muscle Area.Front Nutr. 2022 May 12;9:781860. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.781860. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35634380 Free PMC article.
-
Intra-operator Repeatability of Manual Segmentations of the Hip Muscles on Clinical Magnetic Resonance Images.J Digit Imaging. 2023 Feb;36(1):143-152. doi: 10.1007/s10278-022-00700-0. Epub 2022 Oct 11. J Digit Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36219348 Free PMC article.
-
Abdominal imaging associates body composition with COVID-19 severity.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 13;18(4):e0283506. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283506. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37053189 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

