Fumonisin B1 Production by Fusarium Species and Mycotoxigenic Effect on Larval Zebrafish
- PMID: 33214858
- PMCID: PMC7652242
- DOI: 10.21315/tlsr2020.31.3.7
Fumonisin B1 Production by Fusarium Species and Mycotoxigenic Effect on Larval Zebrafish
Abstract
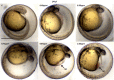
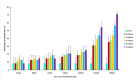
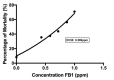
Fumonisin B1 (FB1) is a common mycotoxin produced by Fusarium species particularly F. proliferatum and F. verticillioides. The toxin produced can cause adverse effects on humans and animals. The objectives of this study were to detect the production of FB1 based on the amplification of FUM1 gene, to quantify FB1 produced by the isolates using Ultra-fast Liquid Chromatography (UFLC) analysis, to examine the embryotoxicity effect of FB1 and to determine EC50 toward the larvae of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fifty isolates of Fusarium species were isolated from different hosts throughout Malaysia. Successful amplification of the FUM1 gene showed the presence of this gene (800 bp) in the genome of 48 out of 50 isolates. The highest level of FB1 produced by F. proliferatum isolate B2433 was 6677.32 ppm meanwhile F. verticillioides isolate J1363 was 954.01 ppm. From the assessment of embryotoxicity test of FB1 on larvae of zebrafish, five concentrations of FB1 (0.43 ppm, 0.58 ppm, 0.72 ppm, 0.87 ppm and 1.00 ppm) were tested. Morphological changes of the FB1 exposed-larvae were observed at 24 to 168 hpf. The mortality rate and abnormality of zebrafish larvae were significantly increased at 144 hpf exposure. Meanwhile, the spontaneous tail coiling showed a significant difference. There were no significant differences in the heartbeat rate. As a conclusion, the presence of FUM1 in every isolate can be detected by FUM1 gene analysis and both of the species produced different concentrations of FB1. This is the first report of FB1 produced by Fusarium species gave a significant effect on zebrafish development.
Fumonisin B1 (FB1) ialah mikotoksin biasa yang dihasilkan oleh spesies Fusarium, terutamanya F. proliferatum and F. verticillioides. Toksin yang dihasilkan boleh menyebabkan kesan yang buruk terhadap manusia dan haiwan. Objektif kajian ini adalah untuk mengesan penghasilan FB1 berdasarkan amplifikasi gen FUM1, mengukur kuantiti FB1 yang dihasilkan oleh pencilan menggunakan analisis Kromatografi Cecair Ultra-Cepat (UFLC), memeriksa kesan embriotoksik FB1 dan mengenal pasti EC50 terhadap ikan zebra (Danio rerio). Lima puluh spesies Fusarium diasingkan daripada perumah berlainan di seluruh Malaysia. Amplifikasi gen FUM1 pada 48 daripada 50 pencilan berjaya menunjukkan kehadiran gen ini (800 bp). Pencilan F. proliferatum B2433 menghasilkan FB1 pada aras tertinggi sebanyak 6677.32 bpm manakala pencilan F. verticillioides J1363 sebanyak 954.01 ppm. Berdasarkan penilaian ujian embriotoksik FB1 ke atas larva ikan zebra, lima kepekatan FB1 (0.43 ppm, 0.58 ppm, 0.72 ppm, 0.87 ppm dan 1.00 ppm) telah diuji. Perubahan morfologi larva yang terdedah kepada FB1 diperhatikan pada 24 hingga 168 hpf. Kadar kematian dan ketidaknormalan larva ikan zebra meningkat pada pendedahan 144 hpf. Sementara itu, penggulungan ekor secara spontan menunjukkan perbezaan yang bererti. Tiada perbezaan yang bererti terhadap kadar degupan jantung. Kesimpulannya, kehadiran FUM1 pada setiap pencilan boleh dikesan dengan analisis gen FUM1 dan kedua-dua spesies menghasilkan kepekatan FB1 yang berbeza. Hasil kajian ini merupakan laporan pertama FB1 yang dihasilkan oleh spesies Fusarium yang memberikan kesan yang bererti ke atas perkembangan ikan zebra.
Keywords: Fumonisin B1; Fusarium; Malaysia; Toxic; Ultra-Fast Liquid Chromatography.
© Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia, 2020.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Species composition of and fumonisin production by the Fusarium fujikuroi species complex isolated from Korean cereals.Int J Food Microbiol. 2018 Feb 21;267:62-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.12.006. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Int J Food Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29291460
-
Evaluating three commonly used growth media for assessing fumonisin analogues FB1, FB2 and FB3 production by nine Fusarium verticillioides isolates.Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2017 Feb;34(2):291-298. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2016.1266397. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2017. PMID: 27899061
-
Mycotoxin production by Fusarium proliferatum isolates from rice with Fusarium sheath rot disease.Mycopathologia. 1999;147(2):97-104. doi: 10.1023/a:1007147813326. Mycopathologia. 1999. PMID: 10967968
-
A review and update of animal toxicoses associated with fumonisin-contaminated feeds and production of fumonisins by Fusarium isolates.Mycopathologia. 1992 Feb;117(1-2):109-14. doi: 10.1007/BF00497286. Mycopathologia. 1992. PMID: 1513366 Review.
-
Fumonisin B1 neurotoxicity: Preclinical evidence, biochemical mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Toxicol Rep. 2025 Jan 27;14:101931. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.101931. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39980663 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction of Fumonisin B1, N-Palmitoyl-Fumonisin B1, 5-O-Palmitoyl-Fumonisin B1, and Fumonisin B4 Mycotoxins with Human Serum Albumin and Their Toxic Impacts on Zebrafish Embryos.Biomolecules. 2023 Apr 27;13(5):755. doi: 10.3390/biom13050755. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37238625 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Mycotoxin Contaminations on Aquatic Organisms: Toxic Effect of Aflatoxin B1 and Fumonisin B1 Mixture.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jul 29;14(8):518. doi: 10.3390/toxins14080518. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36006180 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Mycotoxin Family of Fumonisins, Their Biosynthesis, Metabolism, Methods of Detection and Effects on Humans and Animals.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 28;26(1):184. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010184. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39796041 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
