Oral Colonisation after the Administration of Drops Containing Lactobacillus reuteri
- PMID: 33215493
- PMCID: PMC11654502
- DOI: 10.3290/j.ohpd.a45523
Oral Colonisation after the Administration of Drops Containing Lactobacillus reuteri
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the oral colonisation potential after four weeks' administration of Lactobacillus reuteri and to examine the short-term effect of probiotics on salivary Streptococcus mutans and lactobacilli.
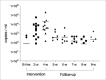
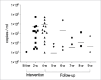
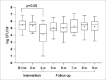
Materials and methods: The study group comprised 13 young adults who volunteered after receiving verbal and written information. The short-term prospective clinical trial lasted 9 weeks, consisting of a 4-week intervention period with administration twice daily and a 5-week post-administration follow-up period with no probiotic consumption. Saliva and dental biofilm samples were obtained immediately before probiotic administration, after 2 weeks and after 4 weeks of L. reuteri administration. Follow-up samples were collected once every week on a regular basis after administration was terminated. The numbers of salivary S. mutans and lactobacilli were assessed by regular plating, while the presence of the two L. reuteri strains in saliva and dental biofilm was evaluated using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR).
Results: The occurrence of L. reuteri in the oral cavity increased gradually during the intervention period and reached the maximum level after four weeks of probiotic administration (p < 0.0001). The 4-week samples of stimulated whole saliva showed a statistically significant decrease in the number of S. mutans and a statistically significant increase in the salivary lactobacilli level in comparison to baseline. qPCR showed that the DSM 17938 strain has better colonisation for both saliva and dental biofilm than the ATCC PTA 5289 strain at the nine-week follow-up.
Conclusion: Probiotics have the ability to colonise the oral cavity during usage, but it gradually disappears after the completion of intake. It also has ability to decrease the number of salivary S. mutans.
Keywords: Lactobacillus reuteri; Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans); dental biofilm; dental plaque; probiotics; qPCR; saliva.
Figures

References
-
- Busscher HJ, Mulder AF, van der Mei HC. In vitro adhesion to enamel and in vivo colonization of tooth surfaces by lactobacilli from a bio-yoghurt. Caries Res. 1999;33:403–404. - PubMed
-
- Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clinical Chem. 2009;55:611–622. - PubMed
-
- Çaglar E, Onder Kuscu O, Selvi Kuvvetli S, Kavaloglu Cildir S, Sandalli N, Twetman S. Short-term effect of ice-cream containing bifidobacterium lactis Bb-12 on the number of salivary mutans streptococci and lactobacilli. Acta Odontol Scand. 2009;66:154–158. - PubMed
-
- Çaglar E, Topcuoglu N, Cildir SK, Sandalli N, Kulekci G. Oral colonization by lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 after exposure to probiotics. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2009;19:377–381. - PubMed
-
- Cildir SK, Germec D, Sandalli N, Ozdemir FI, Arun T, Twetman S. Reduction of salivary mutans streptococci in orthodontic patients during daily consumption of yoghurt containing probiotic bacteria. EORTHO. 2009;4:407–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

