Resveratrol alleviates alveolar epithelial cell injury induced by hyperoxia by reducing apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction
- PMID: 33215523
- PMCID: PMC7934147
- DOI: 10.1177/1535370220975106
Resveratrol alleviates alveolar epithelial cell injury induced by hyperoxia by reducing apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction
Abstract
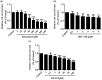
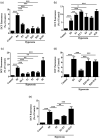
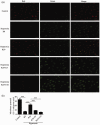
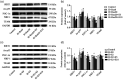
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia is a severe and long-term pulmonary disease in premature infants. Hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury plays a critical role in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Resveratrol is a polyphenolic phytoalexin and a natural agonist of Sirtuin 1. Many studies have shown that resveratrol has a protective effect on hyperoxia-induced lung damage, but its specific protective mechanism is still not clear. Further exploration of the possible protective mechanism of resveratrol was the main goal of this study. In this study, human alveolar epithelial cells were used to establish a hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury cell model, and resveratrol (Res or R), the Sirtuin 1 activator SRT1720 (S) and the Sirtuin 1 inhibitor EX-527 (E) were administered to alveolar epithelial cells, which were then exposed to hyperoxia to investigate the role of Res in mitochondrial function and apoptosis. We divided human alveolar epithelial cells into the following groups: (1) the control group, (2) hyperoxia group, (3) hyperoxia+Res20 group, (4) hyperoxia+Res20+E5 group, (5) hyperoxia+Res20+E10 group, (6) hyperoxia+S2 group, (7) hyperoxia+S2+E5 group, and (8) hyperoxia+S2+E10 group. Hyperoxia-induced cell apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction were alleviated by Res and SRT1720. Res and SRT1720 upregulated Sirtuin 1, PGC-1α, NRF1, and TFAM but decreased the expression of acetyl-p53 in human alveolar epithelial cells that were exposed to hyperoxia. These findings revealed that Res may alleviated hyperoxia-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells through the SIRT1/PGC-1a signaling pathway. Thus, Sirtuin 1 upregulation plays an important role in lung protection.
Keywords: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia; EX-527; SRT1720; apoptosis; mitochondrial dysfunction; resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Resveratrol Attenuates Hyperoxia Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats by Activating SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling Pathway.Am J Perinatol. 2024 Jun;41(8):1039-1049. doi: 10.1055/a-1787-3396. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Am J Perinatol. 2024. PMID: 35240708
-
The protective role of resveratrol on hyperoxia-induced renal injury in neonatal rat by activating the SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 15;993:177364. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177364. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39947344
-
Protective effect of resveratrol on mitochondrial biogenesis during hyperoxia-induced brain injury in neonatal pups.BMC Neurosci. 2023 Apr 25;24(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12868-023-00797-1. BMC Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37098490 Free PMC article.
-
Role of mitochondria in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Influencing the NAD+-dependent SIRT1-PGC-1α-TFAM pathway.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019;145:177-209. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Jun 8. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31208524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural products and phytochemical nanoformulations targeting mitochondria in oncotherapy: an updated review on resveratrol.Biosci Rep. 2020 Apr 30;40(4):BSR20200257. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200257. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32163546 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive value of serum MED1 and PGC-1α for bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Jul 28;24(1):363. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03145-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39069619 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA gadd7 promotes mitochondrial membrane potential decrease and apoptosis of alveolar type II epithelial cells by positively regulating MFN1 in an in vitro model of hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury.Eur J Histochem. 2023 May 31;67(2):3535. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2023.3535. Eur J Histochem. 2023. PMID: 37254890 Free PMC article.
-
Salvianolic acid A promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and function via regulating the AMPK/PGC-1α signaling pathway in HUVECs.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jun 1;24(1):485. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11412. eCollection 2022 Jul. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35761806 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Hyperoxia on Mitochondrial Homeostasis: Are Mitochondria the Hub for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 30;9:642717. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.642717. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33996802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Azithromycin Mitigates Cisplatin-Induced Lung Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Necroptosis by Upregulating SIRT1, PPARγ, and Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 29;16(1):52. doi: 10.3390/ph16010052. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36678549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakagawa M, Nishizaki N, Endo A, Someya T, Saito Y, Mizutani A, Hara T, Murano Y, Sakuraya K, Hara S, Umino D, Hirano D, Fujinaga S, Ohtomo Y, Shimizu T. Impaired nephrogenesis in neonatal rats with oxygen-induced retinopathy. Pediatr Int 2017; 59:704–10 - PubMed
-
- Chou HC, Chen CM. Neonatal hyperoxia disrupts the intestinal barrier and impairs intestinal function in rats. Exp Mol Pathol 2017; 102:415–21 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

