Stabilization of ERK-Phosphorylated METTL3 by USP5 Increases m6A Methylation
- PMID: 33217317
- PMCID: PMC7720844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.026
Stabilization of ERK-Phosphorylated METTL3 by USP5 Increases m6A Methylation
Abstract
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant mRNA modification and is installed by the METTL3-METTL14-WTAP methyltransferase complex. Although the importance of m6A methylation in mRNA metabolism has been well documented recently, regulation of the m6A machinery remains obscure. Through a genome-wide CRISPR screen, we identify the ERK pathway and USP5 as positive regulators of the m6A deposition. We find that ERK phosphorylates METTL3 at S43/S50/S525 and WTAP at S306/S341, followed by deubiquitination by USP5, resulting in stabilization of the m6A methyltransferase complex. Lack of METTL3/WTAP phosphorylation reduces decay of m6A-labeled pluripotent factor transcripts and traps mouse embryonic stem cells in the pluripotent state. The same phosphorylation can also be found in ERK-activated human cancer cells and contribute to tumorigenesis. Our study reveals an unrecognized function of ERK in regulating m6A methylation.
Keywords: ERK; METTL3 phosphorylation; USP5; m(6)A methylation; stem cell differentiation.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests C.H. is a scientific founder and member of the scientific advisory board of Accent Therapeutics, Inc.
Figures


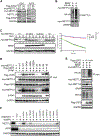
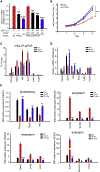
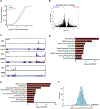
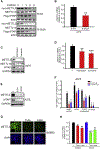

Comment in
-
You Get a Modification, and You Get a Modification… Everyone Gets a Modification!Mol Cell. 2020 Nov 19;80(4):557-559. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.043. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 33217314
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

