Nanoscale platform for delivery of active IRINOX to combat pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 33217475
- PMCID: PMC8008503
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.11.029
Nanoscale platform for delivery of active IRINOX to combat pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Due to its late diagnosis and dismal prognosis, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the most devastating solid malignancies, with only 9% of patients surviving after being diagnosed. A multidrug chemotherapeutic regimen FOL-F-IRIN-OX (combination of 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin) offers survival benefits superior to that of gemcitabine single agent, but the treatment-related side effects are also severe. To overcome this therapeutic barrier, we developed polymeric micelles bearing active formats of irinotecan and oxaliplatin, SN38 and 1,2-diaminocyclohexane‑platinum (II), DACHPt. Crosslinked micelles were prepared using amphiphilic PEG-b-poly(L-glutamic acid)/SN38 conjugates and subsequently loaded with DACHPt. The dual drug-loaded micelles exhibited improved colloidal stability, prolonged drug release and remarkable cytotoxicity in human pancreatic cancer cell lines and KrasG12D; Trp52R172H/+; Pdx-1 Cre murine tumor organoids models. In vivo, (SN38 + DACHPt)-loaded micelles displayed superior antitumor and antimetastatic activities without impairing safety. Our results suggest that nanomedicine mimicking irinotecan and oxaliplatin as parts of FOLFIRINOX regimen may further improve the feasibility of this multidrug treatment for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer.
Keywords: Combination therapy; DACHPt; FOLFIRINOX; Irinotecan; Oxaliplatin; Pancreatic cancer; Polymeric micelles; SN38.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures



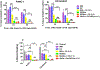
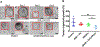
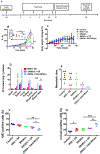
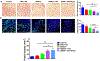
Similar articles
-
A single microbubble formulation carrying 5-fluorouridine, Irinotecan and oxaliplatin to enable FOLFIRINOX treatment of pancreatic and colon cancer using ultrasound targeted microbubble destruction.J Control Release. 2021 Oct 10;338:358-366. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.08.050. Epub 2021 Sep 1. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 34481018
-
First-line liposomal irinotecan with oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin (NALIRIFOX) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A phase I/II study.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Jul;151:14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.03.028. Epub 2021 May 4. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33957442 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of UGT1A1 genetic polymorphism on toxicity in unresectable pancreatic cancer patients undergoing FOLFIRINOX.Cancer Sci. 2019 Feb;110(2):707-716. doi: 10.1111/cas.13883. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30447099 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the FOLFIRINOX regimen for advanced pancreatic cancer.Curr Oncol Rep. 2013 Apr;15(2):182-9. doi: 10.1007/s11912-012-0290-4. Curr Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23341367 Review.
-
The role of FOLFIRINOX in metastatic pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2021 Jun 21;19(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02291-6. World J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34154596 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing Organoid Platforms for Nanoparticle Drug Development.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jul 18;19:6125-6143. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S530999. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40698061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on the Efficacy and Safety of Nab-Paclitaxel with Gemcitabine in Combination with Other Therapeutic Agents as New Treatment Strategies in Pancreatic Cancer.Life (Basel). 2022 Feb 22;12(3):327. doi: 10.3390/life12030327. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35330078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOLFIRINOX Pharmacodynamic Interactions in 2D and 3D Pancreatic Cancer Cell Cultures.AAPS J. 2022 Oct 13;24(6):108. doi: 10.1208/s12248-022-00752-8. AAPS J. 2022. PMID: 36229752
-
Recent Advances in Well-Designed Therapeutic Nanosystems for the Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Treatment Dilemma.Molecules. 2023 Feb 3;28(3):1506. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031506. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36771172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine in Pancreatic Cancer: Current Status and Future Opportunities for Overcoming Therapy Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 7;13(24):6175. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246175. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944794 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pancreatic Cancer: Statistics, Cancer.net, https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/pancreatic-cancer/statistics, (2020).
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM, Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States, Cancer research, 74 (2014) 2913–2921. - PubMed
-
- A.C. Society, Cancer Facts and Figures 2020
-
- Balaban EP, Mangu PB, Yee NS, Locally Advanced Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Summary, Journal of oncology practice, 13 (2016) 265–269. - PubMed
-
- Seufferlein T, Bachet J, Van Cutsem E, Rougier P, Group EGW, Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: ESMO–ESDO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up, Annals of oncology, 23 (2012) vii33–vii40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

