Terpenoids from Marine Soft Coral of the Genus Xenia in 1977 to 2019
- PMID: 33217924
- PMCID: PMC7698640
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25225386
Terpenoids from Marine Soft Coral of the Genus Xenia in 1977 to 2019
Abstract
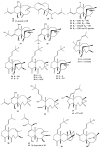
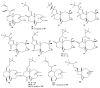
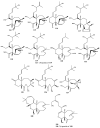
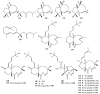
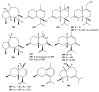
Members of the marine soft coral genus Xenia are rich in a diversity of diterpenes. A total of 199 terpenes consisting of 14 sesquiterpenes, 180 diterpenes, and 5 steroids have been reported to date. Xenicane diterpenes were reported to be the most common chemical skeleton biosynthesized by members of this genus. Most of the literature reported the chemical diversity of Xenia collected from the coral reefs in the South China Sea and the coastal waters of Taiwan. Although there was a brief review on the terpenoids of Xenia in 2015, the present review is a comprehensive overview of the structural diversity of secondary metabolites isolated from soft coral genus Xenia and their potent biological activity as reported between 1977 to 2019.
Keywords: Xenia sp.; bioactivity; marine soft corals; natural products; terpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity of Secondary Metabolites from Soft Coral Genus Sinularia since 2013.Mar Drugs. 2021 Jun 11;19(6):335. doi: 10.3390/md19060335. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34208171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Terpenes from the soft corals of the genus Sarcophyton: chemistry and biological activities.Chem Biodivers. 2013 Dec;10(12):2161-96. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201200122. Chem Biodivers. 2013. PMID: 24327439 Review.
-
Terpenoids from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia multiflora.Nat Prod Res. 2021 Jul;35(14):2395-2402. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2019.1678615. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Nat Prod Res. 2021. PMID: 31631686
-
Terpenoids from Marine Soft Coral of the Genus Lemnalia: Chemistry and Biological Activities.Mar Drugs. 2018 Sep 9;16(9):320. doi: 10.3390/md16090320. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30205594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydroids (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa) from Mauritanian Coral Mounds.Zootaxa. 2020 Nov 16;4878(3):zootaxa.4878.3.2. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.4878.3.2. Zootaxa. 2020. PMID: 33311142
Cited by
-
Chemical Diversity and Biological Activity of Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Indonesian Marine Invertebrates.Molecules. 2021 Mar 27;26(7):1898. doi: 10.3390/molecules26071898. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33801617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards Sustainable Medicinal Resources through Marine Soft Coral Aquaculture: Insights into the Chemical Diversity and the Biological Potential.Mar Drugs. 2022 Oct 14;20(10):640. doi: 10.3390/md20100640. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36286463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive In Silico Study of New Metabolites from Heteroxenia fuscescens with SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitory Activity.Molecules. 2022 Oct 29;27(21):7369. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217369. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364194 Free PMC article.
-
Living Coral Displays, Research Laboratories, and Biobanks as Important Reservoirs of Chemodiversity with Potential for Biodiscovery.Mar Drugs. 2025 Feb 19;23(2):89. doi: 10.3390/md23020089. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 39997213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Terpenoids with Antiangiogenic Activity from Formosan Soft Coral Caementabunda hypotentaculata.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2025 Apr 3;27(2):71. doi: 10.1007/s10126-025-10452-x. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2025. PMID: 40178667
References
-
- Liang L.F., Kurtán T., Mándi A., Yao L.G., Li J., Lan L.F., Guo Y.W. Structural, stereochemical, and bioactive studies of cembranoids from Chinese soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum. Tetrahedron. 2018;74:1933–1941. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2018.02.059. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

