N Partitioning between Gluten Fractions in a Set of Italian Durum Wheat Cultivars: Role of the Grain N Content
- PMID: 33217983
- PMCID: PMC7698631
- DOI: 10.3390/foods9111684
N Partitioning between Gluten Fractions in a Set of Italian Durum Wheat Cultivars: Role of the Grain N Content
Abstract
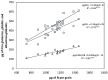
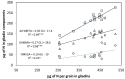
Grain protein content constitutes a key quality trait for durum wheat end-products and may also impact grain protein composition. A total of sixteen durum wheat cultivars were analyzed in a field trial during two seasons at two nitrogen (N) levels to evaluate whether and to what extent the variation in total grain N was associated with variation in the quantity of the various protein fractions and grain quality parameters. Genotypic variation in grain N content correlated with the variation in the content of all three protein fractions, although the strength of the correlation with gliadin and albumin-globulin was higher than that with glutenins. Genotypic variation in gliadin and glutenin content was more tightly correlated with the variation in the sulfur (S)-rich protein groups than with the S-poor protein groups and subunits. The variation in the percentage of unextractable polymeric proteins (UPP%) among genotypes was independent of their glutenin allelic composition. The significant genotypic differences in UPP% and in the ratios between protein groups and subunits were not influenced by the corresponding variation in grain N content. The final grain N content can only account for part of the variation in quality parameters and in the partitioning of total grain N between protein fractions since genotypic differences other than grain N content also contribute to these variations.
Keywords: S-rich/S-poor; durum wheat; gliadin/glutenin; grain N content; grain N partitioning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Gallo G., Bianco M.L., Bognanni R., Saimbene G., Orlando A., Grillo O.S.C.A.R., Saccone R., Venora G. Durum wheat bread: Old sicilian varieties and improved ones; Proceedings of the 5th International Tech. Symp. Food Process. Monit. Technology Bioprocesses Food Qual. Management; Potsdam, Germany. 31 August–2 September 2009; pp. 1128–1138.
-
- Peña R.J., Trethowan R., Pfeiffer W.H., Van Ginkel M. Quality (End-Use) Improvement in Wheat. J. Crop. Prod. 2002;5:1–37. doi: 10.1300/J144v05n01_02. - DOI
-
- Dexter J.E., Matsuo R.R. Influence of protein content on some durum wheat quality parameters. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1977;57:717–727. doi: 10.4141/cjps77-105. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

