Nanobiosensors for the Detection of Novel Coronavirus 2019-nCoV and Other Pandemic/Epidemic Respiratory Viruses: A Review
- PMID: 33218097
- PMCID: PMC7698809
- DOI: 10.3390/s20226591
Nanobiosensors for the Detection of Novel Coronavirus 2019-nCoV and Other Pandemic/Epidemic Respiratory Viruses: A Review
Abstract
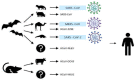
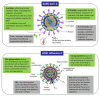
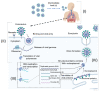
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is considered a public health emergency of international concern. The 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) or severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that caused this pandemic has spread rapidly to over 200 countries, and has drastically affected public health and the economies of states at unprecedented levels. In this context, efforts around the world are focusing on solving this problem in several directions of research, by: (i) exploring the origin and evolution of the phylogeny of the SARS-CoV-2 viral genome; (ii) developing nanobiosensors that could be highly effective in detecting the new coronavirus; (iii) finding effective treatments for COVID-19; and (iv) working on vaccine development. In this paper, an overview of the progress made in the development of nanobiosensors for the detection of human coronaviruses (SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is presented, along with specific techniques for modifying the surface of nanobiosensors. The newest detection methods of the influenza virus responsible for acute respiratory syndrome were compared with conventional methods, highlighting the newest trends in diagnostics, applications, and challenges of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19 causative virus) nanobiosensors.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; SARS/MERS-CoV; coronavirus 2019-nCoV; influenzas; nanobiosensors; nanomaterials; respiratory virus; virus detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative Review of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and Influenza A Respiratory Viruses.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 11;11:552909. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.552909. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33013925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Diagnosis, treatment, control and prevention of SARS-CoV-2 and coronavirus disease 2019: back to the future].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020 Apr 25;36(4):571-592. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200115. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32347053 Review. Chinese.
-
SARS, MERS and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) treatment: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020 Aug;30(8):567-579. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2020.1772231. Epub 2020 Jun 7. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2020. PMID: 32429703 Review.
-
Rapid and sensitive diagnostic procedure for multiple detection of pandemic Coronaviridae family members SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and HCoV: a translational research and cooperation between the Phan Chau Trinh University in Vietnam and University of Bari "Aldo Moro" in Italy.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Jun;24(12):7173-7191. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202006_21713. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32633414
-
Betacoronavirus Genomes: How Genomic Information has been Used to Deal with Past Outbreaks and the COVID-19 Pandemic.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 26;21(12):4546. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124546. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32604724 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic assay and technology advancement for detecting SARS-CoV-2 infections causing the COVID-19 pandemic.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022 Apr;414(9):2903-2934. doi: 10.1007/s00216-022-03918-7. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35211785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosensors as Nano-Analytical Tools for COVID-19 Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Nov 24;21(23):7823. doi: 10.3390/s21237823. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34883826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glyconanomaterials for Human Virus Detection and Inhibition.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jun 26;11(7):1684. doi: 10.3390/nano11071684. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34206886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in point of care testing for COVID-19 detection.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Sep;153:113538. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113538. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36076617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 Biomarkers and Advanced Sensing Technologies for Point-of-Care (POC) Diagnosis.Bioengineering (Basel). 2021 Jul 12;8(7):98. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering8070098. Bioengineering (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356205 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

