The Role of APP O-Glycosylation in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 33218200
- PMCID: PMC7699271
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10111569
The Role of APP O-Glycosylation in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
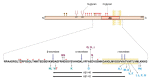
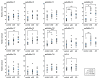
The number of people with dementia is increasing rapidly due to the increase in the aging population. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a type of neurodegenerative dementia caused by the accumulation of abnormal proteins. Genetic mutations, smoking, and several other factors have been reported as causes of AD, but alterations in glycans have recently been demonstrated to play a role in AD. Amyloid-β (Aβ), a cleaved fragment of APP, is the source of senile plaque, a pathological feature of AD. APP has been reported to undergo N- and O-glycosylation, and several Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases (ppGalNAc-Ts) have been shown to have catalytic activity for the transfer of GalNAc to APP. Since O-glycosylation in the proximity of a cleavage site in many proteins has been reported to be involved in protein processing, O-glycans may affect the cleavage of APP during the Aβ production process. In this report, we describe new findings on the O-glycosylation of APP and Aβ production.
Keywords: APP; O-glycan; ppGalNAc-T.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

