Evaluation of two family-based intervention programs for children affected by rare disease and their families - research network (CARE-FAM-NET): study protocol for a rater-blinded, randomized, controlled, multicenter trial in a 2x2 factorial design
- PMID: 33218310
- PMCID: PMC7678588
- DOI: 10.1186/s12875-020-01312-9
Evaluation of two family-based intervention programs for children affected by rare disease and their families - research network (CARE-FAM-NET): study protocol for a rater-blinded, randomized, controlled, multicenter trial in a 2x2 factorial design
Abstract
Background: Families of children with rare diseases (i.e., not more than 5 out of 10,000 people are affected) are often highly burdened with fears, insecurities and concerns regarding the affected child and its siblings. Although families caring for children with rare diseases are known to be at risk for mental disorders, the evaluation of special programs under high methodological standards has not been conducted so far. Moreover, the implementation of interventions for this group into regular care has not yet been accomplished in Germany. The efficacy and cost-effectiveness of a family-based intervention will be assessed.
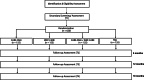
Methods/design: The study is a 2x2 factorial randomized controlled multicenter trial conducted at 17 study centers throughout Germany. Participants are families with children and adolescents affected by a rare disease aged 0 to 21 years. Families in the face-to-face intervention CARE-FAM, online intervention WEP-CARE or the combination of both will be treated over a period of roughly 6 months. Topics discussed in the interventions include coping, family relations, and social support. Families in the control condition will receive treatment as usual. The primary efficacy outcome is parental mental health, measured by the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV (SCID-I) by blinded external raters. Further outcomes will be assessed from the parents' as well as the children's perspective. Participants are investigated at baseline, 6, 12 and 18 months after randomization. In addition to the assessment of various psychosocial outcomes, a comprehensive health-economic evaluation will be performed.
Discussion: This paper describes the implementation and evaluation of two family-based intervention programs for Children Affected by Rare Disease and their Family's Network (CARE-FAM-NET) in German standard care. A methodologically challenging study design is used to reflect the complexity of the actual medical care situation. This trial could be an important contribution to the improvement of care for this highly burdened group.
Trial registration: German Clinical Trials Register: DRKS00015859 (registered 18 December 2018) and ClinicalTrials.gov : NCT04339465 (registered 8 April 2020). Protocol Version: 15 August 2020 (Version 6.1). Trial status: Recruitment started on 1 January 2019 and will be completed on 31 March 2021.
Keywords: Family intervention; Internet-based intervention; Mental health; Randomized controlled trial; Rare diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of a Family-Based Intervention Program for Children of Mentally Ill Parents: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Multicenter Trial.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Jan 20;11:561790. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.561790. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33551858 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Health-Related Quality of Life and Mental Health of Parents With Children and Adolescents With a Rare Disease Based on the Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial to Investigate a Family-Based Intervention and an Online Intervention for Affected Families (CARE-FAM-NET).Fam Process. 2025 Jun;64(2):e70041. doi: 10.1111/famp.70041. Fam Process. 2025. PMID: 40375458 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Early treatment for children with mental health problems and genetic conditions through a parenting intervention (The GAP): study protocol for a pragmatic randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2024 Jul 20;25(1):496. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08278-4. Trials. 2024. PMID: 39033111 Free PMC article.
-
School-based mental health promotion in children and adolescents with StresSOS using online or face-to-face interventions: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial within the ProHEAD Consortium.Trials. 2019 Jan 18;20(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-3159-5. Trials. 2019. PMID: 30658675 Free PMC article.
-
Single-case experimental designs for child neurological rehabilitation and developmental disability research.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2023 May;65(5):611-624. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.15513. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36721909 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of a peer group-based online intervention program in empowering families of children with disabilities at home.Front Pediatr. 2022 Oct 24;10:929146. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.929146. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36353259 Free PMC article.
-
Health-Related Quality of Life and Mental Health of Parents of Children with Pediatric Abdominal Tumors.Children (Basel). 2024 Aug 16;11(8):998. doi: 10.3390/children11080998. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39201933 Free PMC article.
-
Social Resources for Transplanted Children and Families in European Union Hospitals of ERN TransplantChild.Children (Basel). 2021 Aug 24;8(9):723. doi: 10.3390/children8090723. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34572155 Free PMC article.
-
Being the Pillar for Children with Rare Diseases-A Systematic Review on Parental Quality of Life.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 8;18(9):4993. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18094993. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34066738 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of life and mental health of children with rare congenital surgical diseases and their parents during the COVID-19 pandemic.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021 Nov 27;16(1):498. doi: 10.1186/s13023-021-02129-0. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021. PMID: 34838064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Commission. Rare diseases [Internet]. 2005. Available from: http://europa.eu.int/comm/health/ph_threats/non_com/rare_diseases_en.htm.... European Commission, European Union.
-
- Wetterauer B, Schuster R. Seltene Krankheiten - Probleme, Stand und Entwicklung der nationalen und europäischen Forschungsförderung [Rare diseases. Funding programs in Germany and Europe] Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforsch Gesundheitsschutz. 2008;51(5):519–528. doi: 10.1007/s00103-008-0524-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- EURORDIS. Rare diseases: understanding this public health priority [Internet]. 2005. Available from: http://beta.eurordis.org/IMG/pdf/princeps_document-EN.pdf. Accessed 08 October 2019.
-
- Frank M, Eidt-Koch D, Aumann I, Reimann A, Wagner TOF, von der Schulenburg JM. Maßnahmen zur Verbesserung der gesundheitlichen Situation von Menschen mit seltenen Erkrankungen in Deutschland. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2014;57(10):1216–1223. doi: 10.1007/s00103-014-2040-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous