Post-lockdown SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid screening in nearly ten million residents of Wuhan, China
- PMID: 33219229
- PMCID: PMC7679396
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19802-w
Post-lockdown SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid screening in nearly ten million residents of Wuhan, China
Abstract
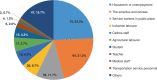
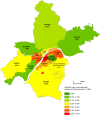
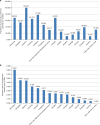
Stringent COVID-19 control measures were imposed in Wuhan between January 23 and April 8, 2020. Estimates of the prevalence of infection following the release of restrictions could inform post-lockdown pandemic management. Here, we describe a city-wide SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid screening programme between May 14 and June 1, 2020 in Wuhan. All city residents aged six years or older were eligible and 9,899,828 (92.9%) participated. No new symptomatic cases and 300 asymptomatic cases (detection rate 0.303/10,000, 95% CI 0.270-0.339/10,000) were identified. There were no positive tests amongst 1,174 close contacts of asymptomatic cases. 107 of 34,424 previously recovered COVID-19 patients tested positive again (re-positive rate 0.31%, 95% CI 0.423-0.574%). The prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Wuhan was therefore very low five to eight weeks after the end of lockdown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Could asymptomatic carriers spread the SARS-CoV-2 infection? Experience from the Italian second wave.J Transl Med. 2021 Mar 2;19(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02762-0. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33653336 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report—51. Data as reported by national authorities by 10 AM CET 11 March 2020 (WHO, 2020).
-
- Prevention measures taken at Sanmin residential community in Wuhan—Xinhua | English.news.cn http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/2020-05/11/c_139048342.htm (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

