Effects and mechanism of platelet-rich plasma on military drill injury: a review
- PMID: 33220706
- PMCID: PMC7680596
- DOI: 10.1186/s40779-020-00285-1
Effects and mechanism of platelet-rich plasma on military drill injury: a review
Abstract
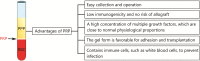
Military drill injury is a significant part of military medical research. The increase of training intensity and changes in training methods lead to differences in injury types. The ideal therapeutic modality should allow rapid healing at a reasonable cost and minimize impact on patients' life. Platelet -rich plasma (PRP), a platelet concentrate, is rich in a variety of growth factors and widely used clinically as a minimally invasive treatment. It plays an important role in injury repair and rehabilitation. In this article, we review the therapeutic role of PRP in military drill injury and its possible underlying mechanisms, with a focus on plantar fasciitis, stress fractures and other common injuries, in order to provide basic support for military reserve.
Keywords: Military drill injury; Plantar fasciitis; Platelet- rich plasma (PRP); Rehabilitation; Stress fracture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gao X, Ding J. The internal structure, main characteristics and great significance of xi Jinping's thought of strengthening the army (in Chinese) Study Pract. 2018;35(1):18–25.
-
- Zhang Q. Thoroughly implement Xi Jinping’s thought of strengthening the army and strive to create a new situation in the cause of national defense mobilization (in Chinese) Natl Def. 2019;8:5–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials