The Sigma-2 receptor / transmembrane protein 97 (σ2R/TMEM97) modulator JVW-1034 reduces heavy alcohol drinking and associated pain states in male mice
- PMID: 33221481
- PMCID: PMC7856185
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108409
The Sigma-2 receptor / transmembrane protein 97 (σ2R/TMEM97) modulator JVW-1034 reduces heavy alcohol drinking and associated pain states in male mice
Abstract
Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) is a chronic relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive alcohol intake, loss of control over alcohol intake, and a negative emotional state when access to alcohol is prevented. AUD is also closely tied to pain, as repeated alcohol drinking leads to increased pain sensitivity during withdrawal. The sigma-2 receptor, recently identified as transmembrane protein 97 (σ2R/TMEM97), is an integral membrane protein involved in cholesterol homeostasis and lipid metabolism. Selective σ2R/Tmem97 modulators have been recently shown to relieve mechanical hypersensitivity in animal models of neuropathic pain as well as to attenuate alcohol withdrawal signs in C. elegans and to reduce alcohol drinking in rats, suggesting a potential key role for this protein in alcohol-related behaviors. In this study, we tested the effects of a potent and selective σ2R/TMEM97 ligand, JVW-1034, on heavy alcohol drinking and alcohol-induced heightened pain states in mice using an intermittent access model. Administration of JVW-1034 decreased both ethanol intake and preference for ethanol, without affecting water intake, total fluid intake, or food intake. Notably, this effect was specific for alcohol, as JVW-1034 had no effect on sucrose intake. Furthermore, JVW-1034 reduced both thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical hypersensitivity in ethanol withdrawn mice. Our data provide important evidence that modulation of σ2R/TMEM97 with small molecules can mediate heavy alcohol drinking as well as chronic alcohol-induced heightened pain sensitivity, thereby identifying a promising novel pharmacological target for AUD and associated pain states.
Keywords: Addiction; Alcoholism; Dependence; Drinking; Ethanol; Hyperalgesia; Pain; Sigma-2 receptor; Transmembrane protein 97.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
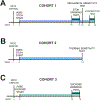
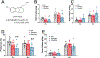

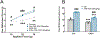
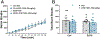
References
-
- 2020. 2018 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH). www.samhsa.gov, pp. Table 5.4A—Alcohol Use Disorder in Past Year among Persons Aged 12 or Older, by Age Group and Demographic Characteristics: Numbers in Thousands, 2017 and 2018.
-
- Abate C, Niso M, Berardi F, 2018. Sigma-2 receptor: past, present and perspectives on multiple therapeutic exploitations. Future Med Chem 10, 1997–2018. - PubMed
-
- Angst MS, Clark JD, 2006. Opioid-induced hyperalgesia: a qualitative systematic review. Anesthesiology 104, 570–587. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

