Outcomes of Hospitalizations for Cardiogenic Shock at Left Ventricular Assist Device Versus Non-Left Ventricular Assist Device Centers
- PMID: 33222608
- PMCID: PMC7763759
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.120.017326
Outcomes of Hospitalizations for Cardiogenic Shock at Left Ventricular Assist Device Versus Non-Left Ventricular Assist Device Centers
Abstract
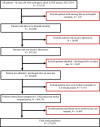
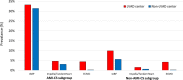
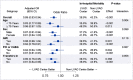
Background Cardiogenic shock (CS) is a complex syndrome associated with high morbidity and mortality. In recent years, many US hospitals have formed multidisciplinary shock teams capable of rapid diagnosis and triage. Because of preexisting collaborative systems of care, hospitals with left ventricular assist device (LVAD) programs may also represent "centers of excellence" for CS care. However, the outcomes of patients with CS at LVAD centers have not been previously evaluated. Methods and Results Patients with CS were identified in the 2012 to 2014 National Inpatient Sample. Clinical characteristics, revascularization rates, and use of mechanical circulatory support were analyzed in LVAD versus non-LVAD centers. The association between hospital type and in-hospital mortality was examined using multivariable logistic regression models. Of 272 075 hospitalizations, 26.0% were in LVAD centers. CS attributable to causes other than acute myocardial infarction represented most cases. In-hospital mortality was lower in LVAD centers (38.9% versus 43.3%; P<0.001). In multivariable analysis, the odds of mortality remained significantly lower for hospitalizations in LVAD centers (odds ratio, 0.89; P<0.001). In patients with CS secondary to acute myocardial infarction, revascularization rates were similar between LVAD and non-LVAD centers. The use of intra-aortic balloon pump (18.7% versus 18.8%) and Impella/TandemHeart (2.6% versus 1.9%) was similar between hospital types, whereas extracorporeal membrane oxygenation was used more frequently in LVAD centers (4.3% versus 0.2%; P<0.001). Conclusions Risk-adjusted mortality was lower in patients with CS who were hospitalized at LVAD centers. These centers likely represent specialized, shock team capable institutions across the country that may be best suited to manage patients with CS.
Keywords: cardiogenic shock; left ventricular assist device; mechanical circulatory support.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Goyal is supported by the National Institute on Aging grant R03AG056446 and American Heart Association grant 18IPA34170185 and is a recipient of a National Institute on Aging Loan Repayment Plan. The remaining authors have no disclosures to report.
Figures
References
-
- Hochman JS, Sleeper LA, Webb JG, Sanborn TA, White HD, Talley JD, Buller CE, Jacobs AK, Slater JN, Col J, et al. Early revascularization in acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock: SHOCK Investigators: Should We Emergently Revascularize Occluded Coronaries for Cardiogenic Shock. N Engl J Med. 1999;625–634. - PubMed
-
- Babaev A, Frederick PD, Pasta DJ, Every N, Sichrovsky T, Hochman JS. Trends in management and outcomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock. JAMA. 2005;448–454. - PubMed
-
- Wayangankar SA, Bangalore S, McCoy LA, Jneid H, Latif F, Karrowni W, Charitakis K, Feldman DN, Dakik HA, Mauri L, et al. Temporal trends and outcomes of patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions for cardiogenic shock in the setting of acute myocardial infarction: a report from the CathPCI Registry. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;341–351. - PubMed
-
- Schrage B, Ibrahim K, Loehn T, Werner N, Sinning JM, Pappalardo F, Pieri M, Skurk C, Lauten A, Landmesser U, et al. Impella support for acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock. Circulation. 2019;1249–1258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

