Risk for cardiovascular disease associated with metabolic syndrome and its components: a 13-year prospective study in the RIVANA cohort
- PMID: 33222691
- PMCID: PMC7680587
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-020-01166-6
Risk for cardiovascular disease associated with metabolic syndrome and its components: a 13-year prospective study in the RIVANA cohort
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate the association of metabolic syndrome (MetS) and its single components with cardiovascular risk and estimated their impact on the prematurity of occurrence of cardiovascular events using rate advancement periods (RAPs).
Methods: We performed prospective analyses among 3976 participants (age range: 35-84, 55% female) in the Vascular Risk in Navarre (RIVANA) Study, a Mediterranean population-based cohort. MetS was defined based on the modified criteria of the American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the International Diabetes Federation. The primary endpoint was major cardiovascular event (a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, or mortality from cardiovascular causes). Secondary endpoints were incidence of non-fatal myocardial infarction and non-fatal stroke, cardiovascular mortality, and all-cause mortality. Cox proportional hazards models, adjusted for potential confounders, were fitted to evaluate the association between MetS and its single components at baseline with primary and secondary endpoints.
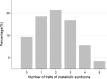
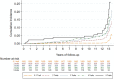
Results: During a median follow-up of 12.8 years (interquartile range, 12.5-13.1), we identified 228 primary endpoint events. MetS was associated with higher risk of incidence of major cardiovascular event, cardiovascular and all-cause mortality, but was neither associated with higher risk of myocardial infarction nor stroke. Compared with participants without MetS, the multivariable hazard ratio (95% confidence interval [CI]) among participants with MetS was 1.32 (1.01-1.74) with RAP (95% CI) of 3.23 years (0.03, 6.42) for major cardiovascular event, 1.64 (1.03-2.60) with RAP of 3.73 years (0.02, 7.45) for cardiovascular mortality, and 1.45 (1.17-1.80) with RAP of 3.24 years (1.21, 5.27) for all-cause mortality. The magnitude of the associations of the single components of MetS was similar than the predicted by MetS. Additionally, for each additional trait of MetS, incidence of major cardiovascular event relatively increased by 22% (1.22, 95% CI 1.09-1.36) with RAP of 2.31 years (0.88, 3.74).
Conclusions: MetS was independently associated with CVD risk, cardiovascular and all-cause mortality. Components of the MetS were associated with similar magnitude of increased CVD, which suggests that MetS was not in excess of the level explained by the presence of its single components. Further research should explore the association of different combinations of the components of MetS with CVD.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Cardiovascular mortality; Cohort study; Mediterranean cohort; Metabolic syndrome; Myocardial infarction; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–88. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kyu HH, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 359 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1859–1922. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32335-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wilkins E, Wilson L, Wickramasinghe K, Bhatnagar P, Leal J, Luengo-Fernandez R, et al. European Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2017. Brussels: European Heart Network, 2017. https://researchportal.bath.ac.uk/en/publications/european-cardiovascula.... Accessed 1 March 2020.
-
- Alberti KGMM, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ, Cleeman JI, Donato KA, et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A Joint Interim Statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation. 2009;120:1640–1645. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192644. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

