Acute kidney injury and renal replacement therapy in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33223467
- PMCID: PMC7608016
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107159
Acute kidney injury and renal replacement therapy in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Reported rates of acute kidney injury (AKI) have varied significantly among studies of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) published to date. The present meta-analysis was conducted to gain clarity regarding AKI incidence and renal replacement therapy (RRT) use in COVID-19 patients.
Methods: The PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, medRxiv, and bioRxiv databases were systematically searched for COVID-19-related case reports published through 25 July 2020. Pooled analyses were conducted using R.
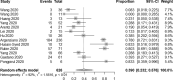
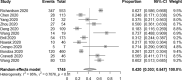
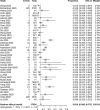
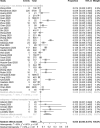
Results: The pooled incidence of AKI in 51 studies including 21,531 patients was 12.3% (95% CI 9.5-15.6%), with higher rates of 38.9% in 290 transplant patients (95% CI 27.3-51.9%), 39.0% in 565 ICU patients (95% CI 23.2-57.6%) and 42.0% among 1745 deceased patients (95% CI 30.3-54.7%). RRT usage was reported in 39 studies of 17,664 patients, with an overall pooled use of 5.4% (95% CI 4.0-7.1%), with higher rates of 15.6% in 117 transplant patients (95%CI 9.9-23.8%) and 16.3% in 776 ICU patients (95% CI 11.1-23.3%).
Conclusion: AKI and RRT use among COVID-19 patients represent a major public health concern, and early and appropriate intervention should be called upon to improve the prognosis of patients suffering from AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; COVID-19; Renal replacement therapy.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
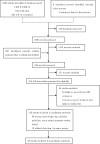
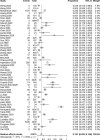
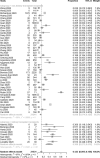


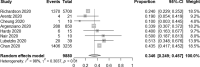

References
-
- COVID-19 Data Repository by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University. https://github.com/CSSEGISandData/COVID-19. 2020 [accessed 31 July 2020].
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

