Barrier Effect of a New Topical Agent on Damaged Esophageal Mucosa: Experimental Study on an ex vivo Swine Model
- PMID: 33223844
- PMCID: PMC7671490
- DOI: 10.2147/CEG.S269568
Barrier Effect of a New Topical Agent on Damaged Esophageal Mucosa: Experimental Study on an ex vivo Swine Model
Abstract
Purpose: AL2106 is a new medical device based on a mixture of chondroitin sulphate in a xyloglucan and glycerol solution made to maximize its bioadhesive capability to the esophageal mucosa. The aim of the present study was twofold to evaluate the AL2106 protective effect on the esophageal mucosa when exposed to an acidic solution mimicking gastric reflux and to assess the resilience of this effect to saline washing.
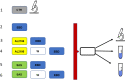
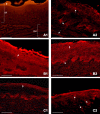
Materials and methods: A porcine ex vivo model was used and the effects of the new medical device were compared to a sodium alginate suspension (SAS) already present on the market which was assumed as reference. Mucosal damage was induced in 19 porcine esophagi by perfusion with an acidic solution added with pepsin, and Evans blue dye (EBD) tissue uptake was used as an indicator of mucosal permeability. The EBD penetration, expressed as EBD µg/g of dry tissue, was assessed in specimens of untreated damaged mucosa and in specimens treated with AL2106 or SAS. The same evaluation was carried out after washing with normal saline.
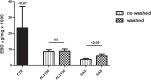
Results: Both topical agents tested significantly reduced the EBD uptake by more than 60% (AL2106 8.4±4.5, SAS 3.6±2.7 vs control 23.2±13.1, p<0.01). The saline washing did not cause any significant reduction in the protective effect of AL2106 (8.6±5.9), while it significantly reduced that of SAS (5.9±4.3, p<0.05).
Conclusion: The new AL2106 medical device showed a good barrier effect against a reflux-like damaging solution and preserved this effect after the mucosal washing test, thus suggesting its possible relevance for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Keywords: EBD; Evans blue dye; GERD; animal model; bioadhesion; esophagus; gastroesophageal reflux disease.
© 2020 Salaroli et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Alfasigma Spa was not involved in the study design, or in the collection, analysis and interpretation of the data. The views expressed in this article are the personal views of the authors and were not influenced by Alfasigma in any way. Alfasigma has agreed with the decision to submit this article for publication. Fiorella Calanni and Antonella Ferrieri are employees of Alfasigma. Maria Laura Bacci reports grants from Alfasigma during the conduct of the study. Fabio Baldi reports personal fees from Alfasigma during the conduct of the study. The authors report no other potential conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rheological Behavior of a New Mucoadhesive Oral Formulation Based on Sodium Chondroitin Sulfate, Xyloglucan and Glycerol.J Funct Biomater. 2021 Apr 28;12(2):28. doi: 10.3390/jfb12020028. J Funct Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33925057 Free PMC article.
-
Barrier effect of Esoxx(®) on esophageal mucosal damage: experimental study on ex-vivo swine model.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2012;5:103-7. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S31404. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22767997 Free PMC article.
-
Protective and regenerative effects of a novel medical device against esophageal mucosal damage using in vitro and ex vivo models.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Nov;131:110752. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110752. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 33152918
-
Esophageal Mucosal Resistance in Reflux Esophagitis: What We Have Learned So Far and What Remains to Be Learned.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Aug 12;13(16):2664. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13162664. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Esophageal impedance monitoring and pathophysiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2006;68(3):151-78. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2006. PMID: 16796016 Review.
Cited by
-
Barrier effect and wound healing activity of the medical device REF-FTP78 in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 12;12(1):6136. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10171-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35414705 Free PMC article.
-
Rheological Behavior of a New Mucoadhesive Oral Formulation Based on Sodium Chondroitin Sulfate, Xyloglucan and Glycerol.J Funct Biomater. 2021 Apr 28;12(2):28. doi: 10.3390/jfb12020028. J Funct Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33925057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sifrim D, Zerbib F. Diagnosis and management of patients with reflux symptoms refractory to proton pump inhibitors. Gut. 2012;61(9):1340–1354. - PubMed
-
- Partial symptom‐response to proton pump inhibitors in patients with non‐erosive reflux disease or reflux oesophagitis – a post hoc analysis of 5796 patients - Bytzer - 2012 - Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics - Wiley Online Library [Internet]. [cited April 23, 2020] Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/apt.12007. Accessed November4, 2020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Topical protection of human esophageal mucosal integrity. American journal of physiology-gastrointestinal and liver physiology [Internet]. [cited April 23, 2020] Available from: https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpgi.00424.2014. Accessed November4, 2020. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

