Is There a Survival Benefit for Patients with Advanced Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Who Complete More Than 6 Cycles of Postoperative Chemotherapy?
- PMID: 33223852
- PMCID: PMC7671476
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S280141
Is There a Survival Benefit for Patients with Advanced Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma Who Complete More Than 6 Cycles of Postoperative Chemotherapy?
Abstract
Purpose: To provide a reference for clinicians, whether patients with advanced ovarian clear cell carcinoma (OCCC) require chemotherapy (CT) for more than 6 cycles after tumor debulking.
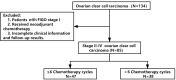
Patients and methods: A retrospective review was performed on 85 women diagnosed and treated for advanced OCCC. Outcomes of patients who underwent >6 vs ≤6 cycles of CT were analyzed based on clinicopathological factors.
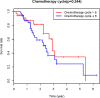
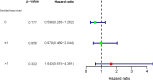
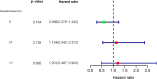
Results: Among the 85 patients with advanced OCCC, 47 patients underwent ≤6 cycles of CT, and 38 patients underwent CT for over 6 cycles. Out of these, 49 patients had disease recurrence, and 35 died. The 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) for patients in the two groups was 51.5% and 42.2% (P>0.05), respectively. The 2-year overall survival (OS) was 59.7% and 64.5%, respectively (P>0.05), and the difference was not statistically significant. Multivariate analysis showed that residual tumor diameter was an independent risk factor for prognosis (PFS and OS). We divided the patients into three groups according to residual tumor diameter as 0 (R0), ≤1cm (R1), and >1cm (R2). The prognosis of R0 was better than R1 and R2. Further studies found that patients who received postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy for over 6 cycles showed no difference in improved prognosis, regardless of residual tumor diameter.
Conclusion: Patients with advanced OCCC who received more than 6 courses of adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery did not show improved prognosis. The residual tumor diameter is an independent indicator of prognosis in patients with advanced OCCC. Complete staging improves the prognosis of patients compared to the ideal or non-ideal cytoreductive surgery.
Keywords: chemotherapy; ovarian clear cell carcinoma; overall survival; prognosis; residual tumor.
© 2020 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing financial interests or conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Residual Tumor Diameter Predicts Progression After Primary Debulking Surgery of Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma (OCCC): Clinicopathologic Study of Stage II-IV OCCC Patients from a Single Institution.Cancer Manag Res. 2021 Mar 4;13:2215-2222. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S293677. eCollection 2021. Cancer Manag Res. 2021. PMID: 33692636 Free PMC article.
-
Ovarian clear cell carcinoma with or without endometriosis origin in a single institution cohort.Discov Oncol. 2023 Apr 1;14(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00649-8. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37004660 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of factors related to the prognostic benefit of neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by interval debulking surgery in patients with advanced ovarian cancer].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Jun 25;56(6):385-392. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112141-20201207-00871. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34154313 Chinese.
-
The surgical, histopathological characteristics, and survival outcome of ovarian clear cell carcinoma: a retrospective case series sharing the experience of a tertiary cancer centre.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):5037-5049. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-83. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39430857 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Adjuvant Chemotherapy on FIGO Stage I Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 May 17;12:811638. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.811638. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35656506 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The impact of varying levels of residual disease following cytoreductive surgery on survival outcomes in patients with ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis.BMC Womens Health. 2024 Mar 15;24(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12905-024-02977-5. BMC Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 38491366 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

