Fear of COVID-19, Stress, and Anxiety in University Undergraduate Students: A Predictive Model for Depression
- PMID: 33224080
- PMCID: PMC7674167
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.591797
Fear of COVID-19, Stress, and Anxiety in University Undergraduate Students: A Predictive Model for Depression
Abstract
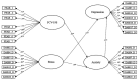
Depression is a disabling illness which increases the risk of suicide. The Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has led to a rise in fear, anxiety, stress, and depression among the population: of these, university undergraduates from countries severely affected by COVID-19 are some of the most vulnerable of all, as they face strict lockdown measures and have fewer resources to cope with it. The aim of this study was to analyze the levels of fear of COVID-19, stress, anxiety, and depression during lockdown among undergraduates from Ecuador, and to test these possible predictors of depression using a model taken from our study of the scientific literature. A total of 640 undergraduates (72% women) between 18 and 47 years old (M = 21.69; S.D = 4.093) were surveyed. The resulting mean levels found for stress, anxiety, and depression were above levels considered non-pathological. Women showed higher levels of fear of COVID-19 than men. The statistical prediction for depression showed a good fit. This depression could be related: both directly and positively by fear of COVID-19 and stress, and indirectly, as a result of these two factors, positively mediated by anxiety. Our study concludes by highlighting the important role that the complex relationships between fear, stress, and anxiety can play in the development of depression symptoms and how they can be taken into account in programs aimed at preventing and alleviating this disorder. We propose some general measures for reducing fear of COVID-19 and stress and suggest that specific programs be designed to control and overcome anxiety among undergraduates.
Keywords: COVID-19; anxiety; depression; fear; stress; undergraduate students.
Copyright © 2020 Rodríguez-Hidalgo, Pantaleón, Dios and Falla.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationships Between Anxiety, Perceived Vulnerability to Disease, and Smartphone Use During Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic in a Sample of Italian College Students.Front Psychol. 2021 Jul 14;12:692503. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.692503. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34335409 Free PMC article.
-
Depression, Anxiety and Stress Associated With Fear of COVID-19 in Peruvian Dental Students: A Multivariate Analysis With 12 Sociodemographic Factors.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2022 Oct 27;13(3):208-220. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_295_21. eCollection 2023 May-Jun. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2022. PMID: 37564168 Free PMC article.
-
Latent profile analysis of COVID-19 fear, depression, anxiety, stress, mindfulness, and resilience.Curr Psychol. 2022;41(1):459-469. doi: 10.1007/s12144-021-01667-x. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Curr Psychol. 2022. PMID: 33821112 Free PMC article.
-
Does Physical Activity Matter for the Mental Health of University Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic?J Clin Med. 2020 Oct 29;9(11):3494. doi: 10.3390/jcm9113494. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33138047 Free PMC article.
-
Noli Timere: The Role of Reassuring Adults in Dealing with COVID-19 Anxiety in Pediatric Age.Pediatr Rep. 2021 Jan 1;13(1):15-30. doi: 10.3390/pediatric13010003. Pediatr Rep. 2021. PMID: 33401500 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post-COVID-19 Syndrome in Outpatients and Its Association with Viral Load.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 17;19(22):15145. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192215145. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36429864 Free PMC article.
-
[Validity and Reliability of the Wong-Law Emotional Intelligence Scale (WLEIS) in Cuban Dental Students in COVID-19 Times].Rev Colomb Psiquiatr. 2022 Nov 21. doi: 10.1016/j.rcp.2022.10.001. Online ahead of print. Rev Colomb Psiquiatr. 2022. PMID: 36440385 Free PMC article. Spanish.
-
Anxiety and Social Support as Predictors of Student Academic Motivation During the COVID-19.Front Psychol. 2021 May 24;12:644338. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.644338. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34108910 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination against COVID-19 reduces virus-related fears: Findings from a German longitudinal study.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 28;10:878787. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.878787. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35968441 Free PMC article.
-
Bibliometric Study of Scientific Productivity on the Impacts on Mental Health in Times of Pandemic.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Dec 24;58(1):24. doi: 10.3390/medicina58010024. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 35056332 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adhikari S. P., Meng S., Wu Y. J., Mao Y. P., Ye R. X., Wang Q. Z., et al. . (2020). Epidemiology, causes, clinical manifestation and diagnosis, prevention and control of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) during the early outbreak period: a scoping review. Infect. Dis. Poverty 9, 1–12. 10.1186/s40249-020-00646-x, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antúnez Z., Vinet E. V. (2012). Escalas de depresión, ansiedad y Estrés (DASS-21): Validación de la Versión abreviada en Estudiantes Universitarios Chilenos. Ter. Psicol. 30, 49–55. 10.4067/S0718-48082012000300005 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources