Macroalgae of Izmir Gulf: Cystoseira barbata, Cystoseira compressa and Cystoseira crinita species have high α-glucosidase and Moderate Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition Activities
- PMID: 33224246
- PMCID: PMC7667568
- DOI: 10.22037/ijpr.2020.1100953
Macroalgae of Izmir Gulf: Cystoseira barbata, Cystoseira compressa and Cystoseira crinita species have high α-glucosidase and Moderate Pancreatic Lipase Inhibition Activities
Abstract
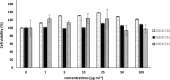
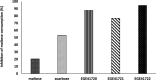
Hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia have been symptoms of many serious diseases such as diabetes and atherosclerosis overall the world. Thus, drug researchers have focused on new, natural and healthy drug alternatives. Marine macroalgae is a great source of hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic or hypocholesterolemic agents. In this study, we investigated that hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic and cytotoxic potentials of 22 marine macroalgae from the Gulf of Izmir. According to our results, the cold methanol extract of Polysiphonia denudata exhibited the highest antioxidant activity (93.6%) compared to BHA (95.3%). Three Cystoseira species, Cystoseria crinita (91.9%), Cystoseria barbata (90.7%), Cystoseria compressa (89.8%) showed higher α-glucosidase inhibition rates than oral antidiabetic acarbose (79.5%). It has also been observed that same species are potent inhibitors of pancreatic lipase. Cytotoxicity test revealed that these extracts did not cause viability inhibition on MCF-7. The results of maltose- glucose assay indirectly displayed that Cystoseira cold methanolic extracts inhibited maltose consumption better than acarbose on HT29. The results of this screening study show that these Cystoseira species may provide non- toxic bioactive agents to control non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: Alpha-glucosidase; Cystoseira; HT29; Inhibitors; Pancreatic lipase.
Figures
References
-
- Association AD. 2. Classification. Diagnosis of Diabetes. Diabetes Care . 2017;40:S11 LP–S24. - PubMed
-
- Saito N, Sakai H, Suzuki S, Sekihara H, Yajima Y. Effect of an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor (voglibose), in combination with sulphonylureas, on glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes patients. J. Int. Med. Res. . 1998;26:219–32. - PubMed
-
- Casirola DM, Ferraris RP. α-Glucosidase inhibitors prevent diet-induced increases in intestinal sugar transport in diabetic mice. Metabolism . 2006;55:832–41. - PubMed
-
- Charpentier G, Dardari D, Riveline JP. How should postprandial glycemia be treated? Diabetes Metab. . 2006;32:2S21–27. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
