Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Omentin-1 and Spexin Levels, Inflammatory Parameters, Lipid Profile, and Anthropometric Indices in Obese and Overweight Adults with Vitamin D Deficiency under Low-Calorie Diet: A Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial
- PMID: 33224249
- PMCID: PMC7673929
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3826237
Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation on Omentin-1 and Spexin Levels, Inflammatory Parameters, Lipid Profile, and Anthropometric Indices in Obese and Overweight Adults with Vitamin D Deficiency under Low-Calorie Diet: A Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background and aims: Improved vitamin D levels can have a favorable effect on some metabolic variables. The objective of the current study was to determine the effects of vitamin D supplementation during a weight-loss intervention on the levels of omentin-1, spexin, lipid profiles, and inflammatory factors in obese and overweight participants.
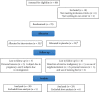
Methods and materials: In this double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial, 70 overweight and obese participants with vitamin D deficiency (25(OH)D ≤ 20 nmol/L) were assigned into the intervention (a daily dose of 2,000 IU vitamin D + low-calorie diet) and placebo (placebo + low-calorie diet) groups for 8 weeks. Anthropometric parameters, serum levels of 25-hydroxy vitamin D (25(OH)D), lipid profiles, omentin-1 and spexin levels, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), and soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) concentrations were assessed before and after the intervention.
Results: Vitamin D supplementation after the intervention led to a significant decrease in triglycerides (TG) (P = 0.02), very-low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (VLDL-C) (P = 0.02), and hs-CRP (P = 0.03) concentrations and a significant increase in the serum vitamin D level (P < 0.001). Furthermore, after adjusting for baseline values, age, and baseline BMI, the levels of serum high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) (P = 0.01) increased significantly, and a significant reduction was observed in the concentration of sICAM-1 (P = 0.01) in the intervention group. However, we did not find any significant difference in serum omentin-1 and spexin concentrations between the groups after intervention.
Conclusions: Vitamin D supplementation along with a low-calorie diet (LCD) program for 8 weeks significantly decreased the inflammatory markers in obese individuals, while it did not alter serum omentin-1 and spexin concentrations.
Copyright © 2020 Elhameh Cheshmazar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Calcium plus vitamin D supplementation affects glucose metabolism and lipid concentrations in overweight and obese vitamin D deficient women with polycystic ovary syndrome.Clin Nutr. 2015 Aug;34(4):586-92. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2014.09.015. Epub 2014 Oct 3. Clin Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25300649 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Probiotic Yogurt on Serum Omentin-1, Adropin, and Nesfatin-1 Concentrations in Overweight and Obese Participants Under Low-Calorie Diet.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019 Dec;11(4):1202-1209. doi: 10.1007/s12602-018-9470-3. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019. PMID: 30232744 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of vitamin D supplementation along with weight loss diet on meta-inflammation and fat mass in obese subjects with vitamin D deficiency: A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2019 Jan;90(1):94-101. doi: 10.1111/cen.13861. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2019. PMID: 30246883 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of 16-weeks vitamin D replacement on calcium-phosphate homeostasis in overweight and obese adults.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Feb;186:169-175. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2018.10.011. Epub 2018 Oct 25. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30367939 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of vitamin D supplementation on serum lipid profiles: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Nutr Rev. 2019 Dec 1;77(12):890-902. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuz037. Nutr Rev. 2019. PMID: 31407792
Cited by
-
Low Vitamin D Status Is Associated with Increased Risk of Mortality in Korean Men and Adults with Hypertension: A Population-Based Cohort Study.Nutrients. 2022 Apr 28;14(9):1849. doi: 10.3390/nu14091849. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35565816 Free PMC article.
-
Aerobic training and vitamin D supplementation effects on diabetes-related parameters in a rat model of type 2 diabetes.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025 Apr 11;17(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13102-025-01125-2. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40217474 Free PMC article.
-
A Randomized Trial with Two Hypocaloric Diets with Different Lipid Profiles and Effects on Serum Omentin-1 Levels in Obese Subjects.Dis Markers. 2022 Mar 7;2022:6777283. doi: 10.1155/2022/6777283. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35295321 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Beta-caryophyllene prevents the defects in trabecular bone caused by Vitamin D deficiency through pathways instated by increased expression of klotho.Bone Joint Res. 2022 Aug;11(8):528-540. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.118.BJR-2021-0392.R1. Bone Joint Res. 2022. PMID: 35920089 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional supplements improve cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese patients: A Bayesian network meta-analysis.Front Nutr. 2023 Mar 30;10:1140019. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1140019. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37063314 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous