A comprehensive review about SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33224265
- PMCID: PMC7664148
- DOI: 10.2217/fvl-2020-0124
A comprehensive review about SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
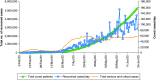
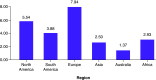
The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) was first identified in China, December 2019. Since then, it has spread the length and breadth of the world at an unprecedented, alarming rate. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV)-2, which causes COVID-19, has much in common with its closest homologs, SARS-CoV and Middle East respiratory syndrome-CoV. The virus-host interaction of SARS-CoV-2 uses the same receptor, ACE2, which is similar to that of SARS-CoV, which spreads through the respiratory tract. Patients with COVID-19 report symptoms including mild-to-severe fever, cough and fatigue; very few patients report gastrointestinal infections. There are no specific antiviral strategies. A few strong medications are under investigation, so we have to focus on proposals which ought to be taken to forestall this infection in a living host.
Keywords: COVID-19; RNA; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; inhibitors; life cycle.
© 2020 Future Medicine Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial & competing interests disclosure The authors have no relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending, or royalties. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in the Nervous System: Implications of COVID-19 in Neurodegeneration.Front Neurol. 2020 Nov 16;11:583459. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.583459. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33304309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological, clinical and epidemiological features of COVID-19, SARS and MERS and AutoDock simulation of ACE2.Infect Dis Poverty. 2020 Jul 20;9(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00691-6. Infect Dis Poverty. 2020. PMID: 32690096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human and novel coronavirus infections in children: a review.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021 Feb;41(1):36-55. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2020.1781356. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021. PMID: 32584199 Review.
-
Current approaches used in treating COVID-19 from a molecular mechanisms and immune response perspective.Saudi Pharm J. 2020 Nov;28(11):1333-1352. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.08.024. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Saudi Pharm J. 2020. PMID: 32905015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Coronavirus With ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme)-2 as Their Main Receptor: Therapeutic Implications.Hypertension. 2020 Nov;76(5):1339-1349. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15256. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32851855 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Virus interactions with the actin cytoskeleton-what we know and do not know about SARS-CoV-2.Arch Virol. 2022 Mar;167(3):737-749. doi: 10.1007/s00705-022-05366-1. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Arch Virol. 2022. PMID: 35102456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Emergence to Endemicity: A Comprehensive Review of COVID-19.Cureus. 2023 Oct 31;15(10):e48046. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48046. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37916248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular interactions of the M and E integral membrane proteins of SARS-CoV-2.Faraday Discuss. 2021 Dec 24;232(0):49-67. doi: 10.1039/d1fd00031d. Faraday Discuss. 2021. PMID: 34543372 Free PMC article.
-
The vital role of animal, marine, and microbial natural products against COVID-19.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):509-524. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2039215. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35234563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of the differences in the binding profile of the wild-type and mutants of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants with the ACE2 receptor.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Nov;138:104936. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104936. Epub 2021 Oct 9. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34655895 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
