MiRNA-610 acts as a tumour suppressor to depress the cisplatin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through targeted silencing of hepatoma-derived growth factor
- PMID: 33224339
- PMCID: PMC7667417
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2019.87938
MiRNA-610 acts as a tumour suppressor to depress the cisplatin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through targeted silencing of hepatoma-derived growth factor
Abstract
Introduction: Hepatic malignancy is one of the most common malignant neoplasms around the globe, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type. In this study, the roles and mechanisms of MiRNA-610 in the chemo resistance of HCC will be discussed.
Material and methods: The expression of MiRNA-610 and hepatoma-derived growth factor (HDGF) in HCC tissues and cell line was detected by quantitative real-time PCR. The proliferation and chemo resistance were analysed by MTT assay. Flow cytometry was used to examine the apoptosis rate. Luciferase reporter assay was used to verify the correlation between MiRNA-610 and HDGF. HDGF protein expression was detected by Western blot.
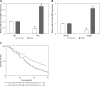
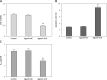
Results: Our study confirmed the low-expression of MiRNA-610 in HCC tissues and cell line. Its low expression was related to high T stages and poor differentiation of HCC, and was a prognostic factor for HCC. MiRNA-610 upregulation inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis of HepG2 cells. MiRNA-610 enhancement decreased the half maximal inhibitory concentration for cisplatin (DDP) and depressed the DDP resistance in HepG2 cells. The specific correlation between MiRNA-610 and HDGF was tested by luciferase reporter assay and western blot. The transfection with HDGF expression vector up-regulated the expression of HDGF protein silenced by MiRNA-610 enhancement. HDGF overexpression was found to reverse partly the regulatory roles of MiRNA-610 on malignancy and DDP resistance.
Conclusions: MiRNA-610 not only played a tumour suppressor role in HCC but also affected chemo resistance to DDP. This role is mainly mediated through targeted silencing of the HDGF gene, which may offer a new potential therapeutic target and improve the clinical therapeutic effect for HCC.
Keywords: MiRNA-610; chemotherapy resistance; hepatocellular carcinoma; hepatoma-derived growth factor.
Copyright: © 2019 Termedia & Banach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tagliamonte M, Petrizzo A, Tornesello ML, Ciliberto G, Buonaguro FM, Buonaguro L. Combinatorial immunotherapy strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016;39:103–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
