Protective potential of curcumin in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rat model: AT1R, mitochondrial DNA synergy
- PMID: 33224436
- PMCID: PMC7675192
Protective potential of curcumin in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rat model: AT1R, mitochondrial DNA synergy
Abstract
Background & objectives: Hypertension can be induced by inhibiting nitric oxide synthesis with L-NAME, which also has a role in oxidative stress. Curcumin has strong antioxidant property. Our aim was to examine the possible preventive role of curcumin on renal dysfunction secondary to hypertension.
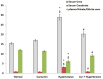
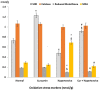
Material & methods: Twenty-four adult male Albino rats were divided in four groups: normal (N); curcumin (C; received curcumin 100 mg/kg/day by oral gavage for 10 weeks); hypertensive (H; received L-NAME 40 mg/kg/day in their drinking water for 4 weeks); and hypertensive-curcumin (HC; received L-NAME and curcumin). Arterial blood pressure was evaluated non-invasively for 4 weeks. Rats were then sacrificed for assessment of oxidative stress (catalase, lipid peroxidase, reduced glutathione and superoxide dismutase), renal function and structure, and biomarkers of apoptosis (Bcl-2 and caspase-3). AT1R expression and renal mtDNA integrity were also assessed.
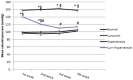
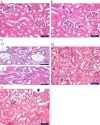
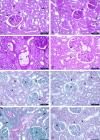
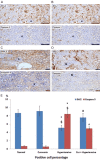
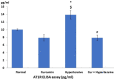
Results: Curcumin attenuated the effects of L-NAME on blood pressure and renal function. The renal histopathological changes observed in the L-NAME group were improved by curcumin administration. The expression of Bcl2 and caspase-3 was improved associated with downregulation of AT1R in curcumin treated groups. The antioxidant markers and mtDNA fragmentation show marked increase in hypertensive group which significantly decreased after curcumin treatment.
Conclusion: Curcumin improved blood pressure elevation renal dysfunction. These improvements mediated through anti-oxidant capabilities and downregulation of AT1R favoring reduced apoptosis and preserved mitochondrial DNA.
Keywords: AT1R; L-NAME; curcumin; mtDNA; oxidative stress; renal function.
IJPPP Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Angiotensin II type 1 receptor on renal NAD(P)H oxidase, oxidative stress and inflammation in nitric oxide inhibition induced-hypertension.Life Sci. 2015 Mar 1;124:81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.01.005. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25623850 Free PMC article.
-
Veratric acid, a phenolic acid attenuates blood pressure and oxidative stress in L-NAME induced hypertensive rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Dec 5;671(1-3):87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.08.052. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21937012
-
Moringa oleifera leaf extract lowers high blood pressure by alleviating vascular dysfunction and decreasing oxidative stress in L-NAME hypertensive rats.Phytomedicine. 2019 Feb 15;54:9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.10.023. Epub 2018 Oct 19. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30668387
-
[Regulatory effect of curcumin on renal apoptosis and its mechanism in overtraining rats].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Jun 8;34(6):513-518. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.5766.2018.115. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 31032585 Chinese.
-
Tetrahydrocurcumin alleviates hypertension, aortic stiffening and oxidative stress in rats with nitric oxide deficiency.Hypertens Res. 2012 Apr;35(4):418-25. doi: 10.1038/hr.2011.180. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Hypertens Res. 2012. PMID: 22072109
Cited by
-
Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Sericin-Derived Oligopeptides (SDOs) from Yellow Silk Cocoons on Blood Pressure Lowering in L-NAME-Induced Hypertensive Rats.Foods. 2025 Apr 3;14(7):1256. doi: 10.3390/foods14071256. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40238512 Free PMC article.
-
Natural compounds targeting mitochondrial dysfunction: emerging therapeutics for target organ damage in hypertension.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 15;14:1209890. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1209890. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37397478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of curcumin on blood pressure and cognitive impairment in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Nutr Res Pract. 2023 Apr;17(2):192-205. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2023.17.2.192. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Nutr Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37009141 Free PMC article.
-
New Therapeutic Insight into the Effect of Ma Huang Tang on Blood Pressure and Renal Dysfunction in the L-NAME-Induced Hypertension.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jul 13;2021:9980429. doi: 10.1155/2021/9980429. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34335852 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring synergistic effects of Achyranthes bidentata Blume and Paeonia lactiflora Pall. on hypertension with liver yang hyperactivity using the multidisciplinary integrative strategy.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 5;10(21):e38649. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38649. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39524820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kitamoto S, Egashira K, Kataoka C, Usui M, Koyanagi M, Takemoto M, Takeshita A. Chronic inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis in rats increases aortic superoxide anion production via the action of angiotensin II. J Hypertens. 2000;18:1795–1800. - PubMed
-
- Tsukahara H, Hiraoka M, Kobata R, Hata I, Ohshima Y, Jiang MZ, Noiri E, Mayumi M. Increased oxidative stress in rats with chronic nitric oxide depletion: measurement of urinary 8-hydroxy-2’-deoxyguanosine excretion. Redox Rep. 2000;5:23–28. - PubMed
-
- Priviero F, Teixeira C, Claudino M, De Nucci G, Zanesco A, Antunes E. Vascular effects of long-term propranolol administration after chronic nitric oxide blockade. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;571:189–196. - PubMed
-
- Correa F, Buelna-Chontal M, Hernández-Reséndiz S, García-Niño WR, Roldán FJ, Soto V, Silva-Palacios A, Amador A, Pedraza-Chaverrí J, Tapia E, Zazueta C. Curcumin maintains cardiac and mitochondrial function in chronic kidney disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;61:119–129. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
