Comparison of efficacy between sequential ventilation and conventional invasive mechanical ventilation in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension complicated with respiratory failure
- PMID: 33224567
- PMCID: PMC7675131
Comparison of efficacy between sequential ventilation and conventional invasive mechanical ventilation in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension complicated with respiratory failure
Abstract
Objective: Pulmonary hypertension (PAH) is a serious progressive and fatal pulmonary disease characterized by elevated pulmonary artery pressure. Mechanical sequential ventilation has been gradually applied in the treatment of patients with PAH complicated with RF, which can effectively reduce the incidence of VAP and better promote the recovery of respiratory function. This study is aimed to determine the efficacy of sequential ventilation and conventional invasive mechanical ventilation in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension (PAH) complicated with respiratory failure (RF).
Methods: A total of 198 patients with both PAH and RF admitted to our hospital were enrolled. Among them, 102 patients were treated with sequential ventilation as a study group (stu group), and 96 patients were treated with conventional invasive mechanical ventilation as a control group (con group). Then the two groups were compared in efficacy and related indexes before and after treatment.
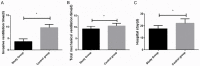
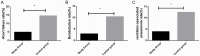
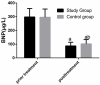
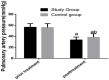
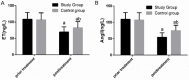
Results: The stu group experienced significantly shorter invasive ventilation time, total mechanical ventilation time, and hospitalization time than the con group (all P<0.05), and showed a significantly lower complication rate than the con group (P<0.05). The reintubation rate, weaning failure rate, and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) rate of the stu group were all significantly lower than those of the con group (all P<0.05), and the stu group showed significantly higher pondus hydrogenii (pH) and arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) and significantly lower arterial carbondioxide partial pressure (PaCO2) than the con group after treatment (all P<0.05). Additionally, after treatment, the level of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and pulmonary artery pressure in both groups declined significantly (P<0.05), and the decline of them in the stu group was more significant than that in the con group (P<0.05). Moreover, after treatment, endothelin (ET) and angiotensin II (Ang II) in both groups declined significantly, and the decline of them in the stu group was also more significant than that in the con group (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Compared with conventional invasive mechanical ventilation, sequential ventilation can effectively minimize the treatment time of patients with PAH complicated with RF, reduce the incidences of adverse events and complications in them, and significantly improve the blood gas analysis indexes and BNP in them, so it is worthy of clinical promotion.
Keywords: Sequential ventilation; brain natriuretic peptide; conventional invasive mechanical ventilation; pulmonary hypertension; respiratory failure.
AJBR Copyright © 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Procalcitonin kinetics to guide sequential invasive-noninvasive mechanical ventilation weaning in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and respiratory failure: procalcitonin's adjunct role.Libyan J Med. 2021 Dec;16(1):1961382. doi: 10.1080/19932820.2021.1961382. Libyan J Med. 2021. PMID: 34357857 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Analysis of clinical effects of early enteral nutrition standardized treatment process management on patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease on invasive mechanical ventilation].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Jan;32(1):67-71. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20190927-00012. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32148234 Chinese.
-
[Application of sequential noninvasive following invasive mechanical ventilation in COPD patients with severe respiratory failure by investigating the appearance of pulmonary-infection-control-window].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006 Feb;31(1):120-4. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006. PMID: 16562692 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Sequential non-invasive following short-term invasive mechanical ventilation in the treatment of tuberculosis with respiratory failure: a randomized controlled study.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Jun 23;21(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01563-x. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 34162374 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Interpreting Real-Time Pulmonary Graphics in Neonatal Invasive Conventional Mechanical Ventilation.Turk Arch Pediatr. 2021 Jul 1;56(4):285-294. doi: 10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2021.21103. eCollection 2021 Jul. Turk Arch Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 35005721 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Sequential treatment of severe pneumonia with respiratory failure and its influence on respiratory mechanical parameters and hemodynamics.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Jul 26;10(21):7314-7323. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i21.7314. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36157993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liyan C, Min P, Nan L, Hua W, Chunli L, Nuofu Z, Wang J. Pulmonary arterial hypertension as the initial pulmonary manifestation in a patient with primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: a case report. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2019;12:1122–1126.
-
- Palazzini M, Dardi F, Manes A, Bacchi Reggiani ML, Gotti E, Rinaldi A, Albini A, Monti E, Galie N. Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease: analysis of survival according to the haemodynamic classification of the 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines and insights for future changes. Eur J Heart Fail. 2018;20:248–255. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitaki A, Boutsikou M, Anthi A, Apostolopoulou S, Avgeropoulou A, Demerouti E, Farmakis D, Feloukidis C, Giannakoulas G, Karvounis H, Karyofyllis P, Mitrouska I, Mouratoglou S, Naka KK, Orfanos SE, Panagiotidou E, Pitsiou G, Rammos S, Stagaki E, Stanopoulos I, Thomaidi A, Triantafyllidi H, Tsangaris I, Tsiapras D, Voudris V, Manginas A Hellenic Society for the Study of Pulmonary Hypertension (HSSPH) Epidemiology and initial management of pulmonary arterial hypertension: real-world data from the Hellenic pulmOnary hyPertension rEgistry (HOPE) Pulm Circ. 2019;9:2045894019877157. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
