Prognostic significance of the Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score in surgically treated breast cancer patients
- PMID: 33224812
- PMCID: PMC7667092
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-20-294
Prognostic significance of the Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score in surgically treated breast cancer patients
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancy in women with high mortality rate. Given the growing evidence shows that immune-inflammatory system influences the survival of patients with cancer, we assessed the prognostic significance of the preoperative Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score in patients with breast cancer who underwent surgery.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of 1,367 breast cancer patients who underwent surgery between December 2010 and October 2012. All individual preoperative serum albumin concentration, total cholesterol concentration, and total peripheral lymphocyte count were counted to calculate CONUT. Higher CONUT score is in line with worse nutritional status. The optimal cut-off of CONUT score was set at 3 to categorize the investigated patients into two groups, namely a high- or low-CONUT score group. We adopted univariate and multivariate analyses (Cox proportional hazards regression model) statistical method.
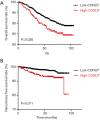
Results: Patients in the high-CONUT score group had shorter overall survival (OS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) in comparison with those in the low-CONUT score group, 66.43 vs. 69.30 months and 54.70 vs. 59.98 months respectively (all P value <0.05). Univariate and multivariate analyses revealed that the CONUT score was an independent predictor of OS (P=0.029 and 0.046, respectively) and RFS (P=0.001, P=0.013, respectively).
Conclusions: The CONUT score was identified as an independent prognostic indicator in surgically treated breast cancer patients, indicating that, compared with the low CONUT score, a high CONUT score may lead to poorer prognosis.
Keywords: CONUT; breast cancer; surgery; survival.
2020 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/gs-20-294). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Significance of Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as a Novel Prognostic Parameter in Small Cell Lung Cancer.Lung. 2020 Aug;198(4):695-704. doi: 10.1007/s00408-020-00361-2. Epub 2020 May 19. Lung. 2020. PMID: 32424800
-
The pretreatment Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score is an independent prognostic factor in patients with resectable thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: results from a retrospective study.BMC Cancer. 2016 Sep 6;16(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2696-0. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27599460 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter Study of Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score as a Prognostic Factor in Patients With HIV-Related Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 30;12:778746. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.778746. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34917092 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Potential of the Preoperative Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score in Predicting Survival of Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review.Adv Nutr. 2021 Feb 1;12(1):234-250. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmaa102. Adv Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32910812 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of the pre-treatment controlling nutritional status score in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jul 2;100(26):e26488. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026488. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34190175 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) as a Novel Postoperative Prognostic Marker in Breast Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Dec 9;2022:3254581. doi: 10.1155/2022/3254581. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36531650 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of CRP-Albumin-Lymphocyte (CALLY) Index in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Breast Cancer.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Mar 15;17:997-1005. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S447201. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 38505146 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of the controlling nutritional status score in patients with hematologic malignancies: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 5;13:952802. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.952802. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275665 Free PMC article.
-
Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Nutritional Status in Women with Breast Cancer: What Is Their Impact on Disease Progression and Recurrence-Free Patients' Survival?Curr Oncol. 2022 Oct 6;29(10):7482-7497. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29100589. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36290866 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of controlling nutritional status score in postoperative recurrence and metastasis of breast cancer patients with HER2-low expression.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 10;13:1116631. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1116631. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37492470 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources