Prognostic significance of the primary tumor site and immune indexes in patients with estrogen receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer
- PMID: 33224820
- PMCID: PMC7667077
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-20-622
Prognostic significance of the primary tumor site and immune indexes in patients with estrogen receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative breast cancer
Abstract
Background: The ability to predict high risk factors for recurrence after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is controversial. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the prognostic significance of tumor location, tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) level, and pretreatment lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR) in determining the survival of patients with estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer after treatment with NAC.
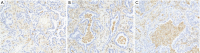
Methods: The clinical data of 285 ER-positive, HER2-negative patients with clinical stage II-III breast cancer were analyzed from January 2009 to January 2015. To explore the prognostic factors for ER-positive, HER2-negative patients, we combined the conventional clinicopathological prognostic factors with tumor location, pretreatment LMR, and TIL. In addition, samples from 79 patients, who did not achieve pathological complete response (pCR) testing after NAC, were selected for hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining to analyze the effect of TIL on prognosis.
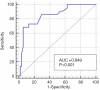
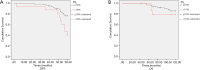
Results: An LMR >5.2 was correlated with better 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS; P<0.001 and P<0.001, respectively). Patients with lower-inner/central quadrant tumors had lower 5-year DFS and OS than patients with tumors in the other quadrants (P=0.012 and P=0.048). Patients with a lower TIL level (≤10%) had better 5-year DFS than patients with a higher TIL level (P=0.010). According to the results of the multivariate analyses, tumor location was an independent prognostic factor for 5-year DFS (P=0.021). Pretreatment LMR was associated with both 5-year DFS and OS (P<0.001 and P<0.001, respectively). In the subgroup analysis stratified by TIL level, the TIL level and the initial clinical stage were associated with 5-year DFS (P=0.027 and P<0.001, respectively).
Conclusions: We explored the prognostic significance of the tumor site, TIL level, and pretreatment LMR level for ER-positive, HER2-negative patients. We concluded that the lower-inner/central quadrant tumors, TIL >10%, and pretreatment LMR level ≤5.2 were correlated with a poor prognosis. More aggressive NAC and/or endocrine therapy with internal mammary node radiotherapy (IMN-RT) should be administered to address the relatively poor prognosis of patients with breast carcinoma presenting the aforementioned adverse factors.
Keywords: Breast cancer; estrogen receptor (ER); human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2); lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR); neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC); tumor site; tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL).
2020 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Both authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/gs-20-622). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The poor prognosis of lower-inner quadrant breast cancer in patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Ann Palliat Med. 2020 Jul;9(4):1859-1871. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-1140. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Ann Palliat Med. 2020. PMID: 32576015
-
Association of TILs with clinical parameters, Recurrence Score® results, and prognosis in patients with early HER2-negative breast cancer (BC)-a translational analysis of the prospective WSG PlanB trial.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 May 14;22(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01283-w. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32408905 Free PMC article.
-
Association of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy with pathological complete response and prognosis in patients with breast cancer.Cancer Med. 2021 Nov;10(22):7921-7933. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4302. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34562054 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram to predict pathologic complete response (pCR) and the value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) for prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) in breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan;173(2):255-266. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4981-x. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30324273 Review.
-
Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2020 Mar 4;20(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-6668-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32131780 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oncoplastic Breast Conservation for Central Tumors: Definition, Classification, and the Analysis of Single Institution Experience.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024 May 6;12(5):e5789. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005789. eCollection 2024 May. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024. PMID: 38712017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Loi S, Sirtaine N, Piette F, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in a phase III randomized adjuvant breast cancer trial in node-positive breast cancer comparing the addition of docetaxel to doxorubicin with doxorubicin-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 2013;31:860-7. 10.1200/JCO.2011.41.0902 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
