IgG4 thyroiditis in the Asian population
- PMID: 33224859
- PMCID: PMC7667064
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-20-417
IgG4 thyroiditis in the Asian population
Abstract
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an immune-mediated fibro-inflammatory condition that often causes the formation of tumefactive lesions. The discovery of IgG4-RD linked many well-known isolated conditions as a distinct multi-organ disease, and started an era of promoting investigation and treatment in relevant fields. In the thyroid gland, a subcategory of Hashimoto thyroiditis (HT) with IgG4-rich inflammation was first discovered and named IgG4 thyroiditis by our group. This subtype of HT presents with rapidly progressive clinical manifestations and destructive histopathological features underlying thyroid dysfunction, which are significantly different from the common type of HT. Moreover, other IgG4-rich thyroid conditions in patients with Graves' disease and systemic IgG4-RD have been described. These observations are most frequently reported in the Asian population for unknown reasons. Although recent studies demonstrated that IgG4 thyroiditis is a specific entity independent from IgG4-RD, recognition of this unique subset of thyroid disease has yielded important insights into understanding its pathogenesis and the development of novel therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Asian population; Thyroid; autoimmune thyroid disease; immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4); thyroiditis.
2020 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/gs-20-417). The series “Asian and Western Practice in Thyroid Pathology: Similarities and Differences” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. KK serves as the unpaid Guest Editor of the series and an unpaid editorial board member of Gland Surgery from Sep 2018 to Aug 2020. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
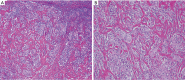
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
