Using the RETAIN Tabletop Simulator as a Summative Assessment Tool for Neonatal Resuscitation Healthcare Professionals: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 33224907
- PMCID: PMC7674399
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2020.569776
Using the RETAIN Tabletop Simulator as a Summative Assessment Tool for Neonatal Resuscitation Healthcare Professionals: A Pilot Study
Abstract
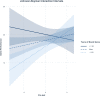
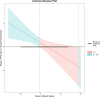
Background: Frequent and objective summative assessment of neonatal healthcare providers is important to ensure high-quality care to patients during neonatal resuscitation. Currently, neonatal resuscitation providers are only individually assessed using an at-home online multiple-choice questionnaire. While simulation-based assessment is preferred, resource constraints limit its widespread uptake. An alternative approach to simulation-based summative assessment is needed. Simulation-based serious games may provide a solution. Objective: The aim of this study was to examine if individual performance on the RETAIN (REsuscitation TrAINing for healthcare professionals) tabletop simulator can be used as a summative assessment of neonatal resuscitation providers, regardless of their prior board game experience. Method: Neonatal healthcare providers were recruited from a tertiary perinatal center to complete a (1) demographic pre-survey, (2) neonatal resuscitation scenario using an open-answer written pre-test, (3) neonatal resuscitation scenario using the RETAIN tabletop simulator, and (4) post-survey measuring usage and attitudes toward board games. Multiple linear regression analyses using the Johnson-Neyman technique were conducted in R to probe the moderation effect of years of board game on the relationship between pre-test and game performance. Results: Twenty Neonatal Resuscitation Program-trained healthcare providers (nurses, nurse practitioners, respiratory therapists, and fellows) were recruited for this study (n = 19 females). Participants' mean (standard deviation) pre-test score was 8.35 (1.81) out of a total 16 possible points (52%) and a score of 18 (4.41) out of a total of 40 possible points (45%) using RETAIN. Overall board game experience was 22.5 (12.6) years. Finally, years of board game moderated significantly the relation between the pre-test and game performance (B = -0.13, SE = 0.05, beta = -0.48, t = -2.77, p < 0.05; 95% CI [-0.24, -0.03]). Thus, participants' performance on the two tests (written and simulator) was significantly positively associated, but only for those who reported fewer than 21.5 years of board game experience. Conclusion: This study reports the preliminary results of a pilot study, indicating that the RETAIN tabletop simulator could be used as a simulation-based summative assessment, an enjoyable, low-cost alternative to traditional assessment approaches. RETAIN offers a solution to the need for more frequent and continued assessment of neonatal resuscitation providers.
Keywords: education; neonatal; resuscitation; simulation; simulation and games; tabletop simulator.
Copyright © 2020 Ghoman, Cutumisu and Schmölzer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simulation-Based Summative Assessment of Neonatal Resuscitation Providers Using the RETAIN Serious Board Game-A Pilot Study.Front Pediatr. 2020 Jan 31;8:14. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.00014. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32083041 Free PMC article.
-
Health Care Providers' Performance, Mindset, and Attitudes Toward a Neonatal Resuscitation Computer-Based Simulator: Empirical Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2020 Dec 21;8(4):e21855. doi: 10.2196/21855. JMIR Serious Games. 2020. PMID: 33346741 Free PMC article.
-
Unsupervised Machine Learning Algorithms Examine Healthcare Providers' Perceptions and Longitudinal Performance in a Digital Neonatal Resuscitation Simulator.Front Pediatr. 2020 Sep 11;8:544. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.00544. eCollection 2020. Front Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 33042905 Free PMC article.
-
The RETAIN Simulation-Based Serious Game-A Review of the Literature.Healthcare (Basel). 2019 Dec 22;8(1):3. doi: 10.3390/healthcare8010003. Healthcare (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31877882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serious games, a game changer in teaching neonatal resuscitation? A review.Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2020 Jan;105(1):98-107. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2019-317011. Epub 2019 Jun 29. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2020. PMID: 31256010 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Virtual simulations for neonatal education.Semin Perinatol. 2023 Nov;47(7):151826. doi: 10.1016/j.semperi.2023.151826. Epub 2023 Sep 24. Semin Perinatol. 2023. PMID: 37770364 Free PMC article.
-
Super Divya, an Interactive Digital Storytelling Instructional Comic Series to Sustain Facilitation Skills of Labor and Delivery Nurse Mentors in Bihar, India-A Pilot Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 25;19(5):2675. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19052675. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35270366 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the use of low-cost simulation in nursing education: a scoping review.BMJ Open. 2025 Jul 17;15(7):e099968. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2025-099968. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40675641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- United Nations Annual Number of Births. United National Children's Fund: The State of the World's Children; (2013). Available online at: http://data.un.org/Data.aspx?d=SOWC&f=inID%3A75 (accessed August 24, 2020).
-
- Weiner GM. Textbook of Neonatal Resuscitation (NRP). 7th ed. Zaichkin J, editor. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics; (2016).
-
- The Joint Commission Sentinel Event Alert: Preventing Infant Death and Injury During delivery. The Joint Commission; (2004). - PubMed
-
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Quality of Health Care in America Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century. National Academies Press; (2001). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

