Krebs von den Lungen 6 decreased in the serum and muscle of GNE myopathy patients
- PMID: 33225515
- PMCID: PMC7983952
- DOI: 10.1111/neup.12703
Krebs von den Lungen 6 decreased in the serum and muscle of GNE myopathy patients
Abstract
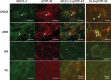
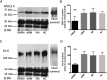
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase (GNE) is necessary for sialic acid biosynthesis. GNE myopathy is caused by a defect in GNE, and hyposialylation is a key factor in the pathomechanism of GNE myopathy. Although candidates for evaluating hyposialylation have been reported, it is difficult to measure them in routine clinical practice. Sialylation is necessary for synthesis of various glycoproteins, including Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6)/mucin 1 (MUC1). Here we report that KL-6/MUC1 is decreased in GNE myopathy. We observed that KL-6 levels were decreased in the serum of patients with GNE myopathy, and that KL-6 and MUC1-C were also decreased in muscle biopsy specimens from these patients. An immunofluorescent study revealed that KL-6 and MUC1-C were not present in the sarcolemma but were, instead, localized in rimmed vacuoles in specimens from patients with GNE myopathy. KL-6 is already used to detect lung diseases in clinical practice, and this glycoprotein may be a novel candidate for evaluating hyposialylation in GNE myopathy.
Keywords: GNE myopathy; KL-6; MUC1; hyposialylation; rimmed vacuoles.
© 2020 The Authors. Neuropathology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Society of Neuropathology.
Figures


References
-
- Nonaka I, Sunohara N, Ishiura S, Satoyoshi E. Familial distal myopathy with rimmed vacuole and lamellar (myeloid) body formation. J Neurol Sci 1981; 51: 141–155. - PubMed
-
- Nishino I, Noguchi S, Murayama K et al. Distal myopathy with rimmed vacuoles is allelic to hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Neurology 2002; 59: 1689–1693. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberg I, Avidan N, Potikha T et al. The UDP–N‐acetylglucosamine 2‐epimerase/N‐acetylmannosamine kinase gene is mutated in recessive hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Nat Genet 2001; 29: 83–87. - PubMed
-
- Keppler OT, Hinderlich S, Langner J, Schwartz‐Albiez R, Reutter W, Pawlita M. UDP–GlcNAc 2‐epimerase: A regulator of cell surface sialylation. Science 1999; 284: 1372–1376. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

