Role of capping agents in the application of nanoparticles in biomedicine and environmental remediation: recent trends and future prospects
- PMID: 33225973
- PMCID: PMC7682049
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-020-00704-4
Role of capping agents in the application of nanoparticles in biomedicine and environmental remediation: recent trends and future prospects
Abstract
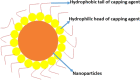
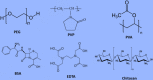
Capping agents are of utmost importance as stabilizers that inhibit the over-growth of nanoparticles and prevent their aggregation/coagulation in colloidal synthesis. The capping ligands stabilize the interface where nanoparticles interact with their medium of preparation. Specific structural features of nanoparticles are attributed to capping on their surface. These stabilizing agents play a key role in altering the biological activities and environmental perspective. Stearic effects of capping agents adsorbed on the surface of nanoparticles are responsible for such changing physico-chemical and biological characteristics. Firstly, this novel review article introduces few frequently used capping agents in the fabrication of nanoparticles. Next, recent advancements in biomedicine and environmental remediation approaches of capped nanoparticles have been elaborated. Lastly, future directions of the huge impact of capping agents on the biological environment have been summarized.
Keywords: Biomedicine; Capping agents; Environment; Nanoparticles; Nanotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Significance of Capping Agents of Colloidal Nanoparticles from the Perspective of Drug and Gene Delivery, Bioimaging, and Biosensing: An Insight.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 10;23(18):10521. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810521. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sustainable Synthesis of Novel Green-Based Nanoparticles for Therapeutic Interventions and Environmental Remediation.ACS Synth Biol. 2024 Jul 19;13(7):1994-2007. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.4c00206. Epub 2024 Jun 20. ACS Synth Biol. 2024. PMID: 38899943 Review.
-
Actinobacteria mediated synthesis of nanoparticles and their biological properties: A review.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016;42(2):209-21. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2014.917069. Epub 2014 Nov 28. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 25430521 Review.
-
Potential applications of engineered nanoparticles in medicine and biology: an update.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2018 Dec;23(8):1185-1204. doi: 10.1007/s00775-018-1600-6. Epub 2018 Aug 10. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 30097748 Review.
-
Tetrazoles: Unique Capping Ligands and Precursors for Nanostructured Materials.Small. 2015 Nov 18;11(43):5728-39. doi: 10.1002/smll.201501630. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Small. 2015. PMID: 26395565
Cited by
-
Biogenic synthesis of selenium nanoparticles from Nyctanthes arbor-tristis L. and evaluation of their antimicrobial, antioxidant and photocatalytic efficacy.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 8;10(12):e32499. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32499. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39183842 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis and Biomedical Application.Molecules. 2023 Dec 15;28(24):8125. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248125. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of Bioactive Silver Nanoparticles Using New Bacterial Strains from an Antarctic Consortium.Mar Drugs. 2022 Aug 31;20(9):558. doi: 10.3390/md20090558. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36135747 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Capping Agents of Colloidal Nanoparticles from the Perspective of Drug and Gene Delivery, Bioimaging, and Biosensing: An Insight.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 10;23(18):10521. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810521. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the in vitro antibacterial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, anticancer and antiviral activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles biofabricated from Cassia javanica.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 1;19(10):e0310927. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310927. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39352889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang S, Zhou L, Zheng Y, Li L, Wu C, Yang H, Huang M, An X. Synthesis and biocompatibility of two-dimensional biomaterials. Colloids Surf A. 2019;583:124004. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124004. - DOI
-
- Gulati S, Sachdeva M, Bhasin KK. Capping agents in nanoparticle synthesis: surfactant and solvent system. AIP Conf Proc. 2018;1953:030214. doi: 10.1063/1.5032549. - DOI
-
- Aisida SO, Batool A, Khan FM, Rahman L, Mahmood A, Ahmad I, et al. Calcination induced PEG-Ni-ZnO nanorod composite and its biomedical applications. Mater Chem Phys. 2020;255:123603. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123603. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

