Prioritised endpoints for device-based hypertension trials: the win ratio methodology
- PMID: 33226002
- PMCID: PMC9724872
- DOI: 10.4244/EIJ-D-20-01090
Prioritised endpoints for device-based hypertension trials: the win ratio methodology
Abstract
Aims: Multiple endpoints with varying clinical relevance are available to establish the efficacy of device-based treatments. Given the variance among blood pressure measures and medication changes in hypertension trials, we performed a win ratio analysis of outcomes in a sham-controlled, randomised trial of renal denervation (RDN) in patients with uncontrolled hypertension despite commonly prescribed antihypertensive medications. We propose a novel prioritised endpoint framework for determining the treatment benefit of RDN compared with sham control.
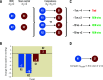
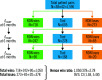
Methods and results: We analysed the SPYRAL HTN-ON MED pilot study data using a prioritised hierarchical endpoint comprised of 24-hour mean ambulatory systolic blood pressure (SBP), office SBP, and medication burden. A generalised pairwise comparisons methodology (win ratio) was extended to examine this endpoint. Clinically relevant thresholds of 5 and 10 mmHg were used for comparisons of ambulatory and office SBP, respectively, and therefore to define treatment "winners" and "losers". For a total number of 1,596 unmatched pairs, the RDN subject was the winner in 1,050 pairs, the RDN subject was the loser in 378 pairs, and 168 pairs were tied. The win ratio in favour of RDN was 2.78 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.58 to 5.48; p<0.001) and corresponding net benefit statistic was 0.42 (95% CI: 0.20 to 0.63). Sensitivity analyses performed with differing blood pressure thresholds and according to drug adherence testing demonstrated consistent results.
Conclusions: The win ratio method addresses prior limitations by enabling inclusion of more patient-oriented results while prioritising those endpoints considered most clinically important. Applying these methods to the SPYRAL HTN-ON MED pilot study (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02439775), RDN was determined to be superior regarding a hierarchical endpoint and a "winner" compared with sham control patients.
Conflict of interest statement
D. Kandzari reports institutional research/grant support from Medtronic and Ablative Solutions, and personal consulting honoraria from Medtronic. G. Hickey, S. Cohen, M. Fahy, and G. Lamberti are employees and shareholders of Medtronic. S. Pocock reports consultant fees from Medtronic outside the submitted work. M.A. Weber reports personal fees from Medtronic, Ablative Solutions, ReCor, and Boston Scientific, all outside the submitted work. M. Böhm reports personal fees from Amgen, Bayer, Servier, Medtronic, Boehringer Ingelheim, Vifor, Bristol Myers Squibb, and AstraZeneca, all outside the submitted work. F. Mahfoud is supported by Deutsche Gesellschaft für Kardiologie (DGK), and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB TRR219) and has received scientific support and speaker honoraria from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Medtronic and ReCor Medical.
Figures
References
-
- Milojevic M, Head SJ, Andrinopoulou ER, Serruys PW, Mohr FW, Tijssen JG, Kappetein AP. Hierarchical testing of composite endpoints: applying the win ratio to percutaneous coronary intervention versus coronary artery bypass grafting in the SYNTAX trial. EuroIntervention. 2017;13:106–14. doi: 10.4244/EIJ-D-16-00745. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Capodanno D, Gargiulo G, Buccheri S, Chieffo A, Meliga E, Latib A, Park SJ, Onuma Y, Capranzano P, Valgimigli M, Narbute I, Makkar RR, Palacios IF, Kim YH, Buszman PE, Chakravarty T, Sheiban I, Mehran R, Naber C, Margey R, Agnihotri A, Marra S, Leon MB, Moses JW, Fajadet J, Lefevre T, Morice MC, Erglis A, Alfieri O, Serruys PW, Colombo A, Tamburino C DELTA Investigators. Computing Methods for Composite Clinical Endpoints in Unprotected Left Main Coronary Artery Revascularization: A Post Hoc Analysis of the DELTA Registry. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;9:2280–8. - PubMed
-
- Hara H, van Klaveren D, Takahashi K, Kogame N, Chichareon P, Modolo R, Tomaniak M, Ono M, Kawashima H, Wang R, Gao C, Niethammer M, Fontos G, Angioi M, Ribeiro VG, Barbato E, Leandro S, Hamm C, Valgimigli M, Windecker S, Jüni P, Steg PG, Verbeeck J, Tijssen JGP, Sharif F, Onuma Y, Serruys PW GLOBAL LEADERS Trial Investigators. Comparative Methodological Assessment of the Randomized GLOBAL LEADERS Trial Using Total Ischemic and Bleeding Events. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020;13:e006660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

