Integrative analysis of structural variations using short-reads and linked-reads yields highly specific and sensitive predictions
- PMID: 33226985
- PMCID: PMC7721175
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008397
Integrative analysis of structural variations using short-reads and linked-reads yields highly specific and sensitive predictions
Abstract
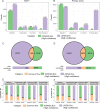
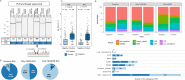
Genetic diseases are driven by aberrations of the human genome. Identification of such aberrations including structural variations (SVs) is key to our understanding. Conventional short-reads whole genome sequencing (cWGS) can identify SVs to base-pair resolution, but utilizes only short-range information and suffers from high false discovery rate (FDR). Linked-reads sequencing (10XWGS) utilizes long-range information by linkage of short-reads originating from the same large DNA molecule. This can mitigate alignment-based artefacts especially in repetitive regions and should enable better prediction of SVs. However, an unbiased evaluation of this technology is not available. In this study, we performed a comprehensive analysis of different types and sizes of SVs predicted by both the technologies and validated with an independent PCR based approach. The SVs commonly identified by both the technologies were highly specific, while validation rate dropped for uncommon events. A particularly high FDR was observed for SVs only found by 10XWGS. To improve FDR and sensitivity, statistical models for both the technologies were trained. Using our approach, we characterized SVs from the MCF7 cell line and a primary breast cancer tumor with high precision. This approach improves SV prediction and can therefore help in understanding the underlying genetics in various diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: Ugur Sahin is co-founder and shareholder of TRON, co-founder and CEO of BioNTech SE.
Figures


References
-
- Nowell C. The minute chromosome (Ph1) in chronic granulocytic leukemia. Blut 1962; 8(2):65–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

