Diagnostic Performance of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) in the Evaluation of Solid Renal Masses
- PMID: 33227984
- PMCID: PMC7699268
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina56110624
Diagnostic Performance of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) in the Evaluation of Solid Renal Masses
Abstract
Background: The present study aims to evaluate the diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) for discriminating between benign and malignant solid renal masses.
Methods: 18 patients with histopathologically confirmed benign solid renal masses (11 oncocytomas, seven angiomyolipomas) as well as 96 patients with confirmed renal cell carcinoma (RCC) who underwent CEUS followed by radical or partial nephrectomy were included in this single-center study. CEUS examinations were performed by an experienced radiologist (EFSUMB Level 3) and included the application of a second-generation contrast agent.
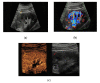
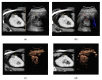
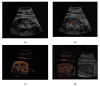
Results: Renal angiomyolipomas, oncocytomas, and renal cell carcinomas showed varying sonomorphological characteristics in CEUS. Angiomyolipomas showed heterogeneous echogenicity (57% hypo-, 43% hyperechoic), while all lesions showed rapid contrast-enhancement with two lesions also showing venous wash-out (29%). Notably, 9/11 oncocytomas could be detected in conventional ultrasound (64% hypo-, 9% hyper-, 9% isoechoic) and 2/11 only demarcated upon intravenous application of contrast agent (18%). All oncocytomas showed hyperenhancement in CEUS, venous wash-out was registered in 7/11 lesions (64%).
Conclusions: In line with the current state of knowledge, no specific sonomorphological characteristics allowing for accurate distinction between benign and malignant solid renal masses in CEUS could be detected in our study.
Keywords: CEUS; contrast-enhanced ultrasound; renal angiomyolipoma; renal cell carcinoma; renal oncocytoma; solid renal mass.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jamis-Dow C.A., Choyke P.L., Jennings S.B. Small (< or = 3-cm) renal masses: Detection with CT versus US and pathologic correlation. Radiology. 1996;198:785–788. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

