SWI/SNF Alterations in Squamous Bladder Cancers
- PMID: 33227989
- PMCID: PMC7699259
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11111368
SWI/SNF Alterations in Squamous Bladder Cancers
Abstract
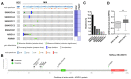
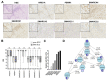
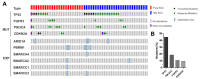
Dysfunction of the SWI/SNF complex has been observed in various cancers including urothelial carcinomas. However, the clinical impact of the SWI/SNF complex in squamous-differentiated bladder cancers (sq-BLCA) remains unclear. Therefore, we aimed to analyze potential expression loss and genetic alterations of (putative) key components of the SWI/SNF complex considering the co-occurrence of genetic driver mutations and PD-L1 expression as indicators for therapeutic implications. Assessment of ARID1A, SMARCA2, SMARCA4, SMARCB1/INI1, SMARCC1, SMARCC2 and PBRM1 mutations in a TCGA data set of sq-BLCA (n = 45) revealed that ARID1A was the most frequently altered SWI/SNF gene (15%) while being associated with protein downregulation. Genetic alterations and loss of ARID1A were confirmed by Targeted Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) (3/6) and immunohistochemistry (6/116). Correlation with further mutational data and PD-L1 expression revealed co-occurrence of ARID1A loss and TP53 mutations, while positive correlations with other driver mutations such as PIK3CA were not observed. Finally, a rare number of sq-BLCA samples were characterized by both ARID1A protein loss and strong PD-L1 expression suggesting a putative benefit upon immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Hence, for the first time, our data revealed expression loss of SWI/SNF subunits in sq-BLCA, highlighting ARID1A as a putative target of a small subgroup of patients eligible for novel therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: ARID1A; SWI/SNF complex; immune checkpoint inhibitors; squamous bladder cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rose M., Maurer A., Wirtz J., Bleilevens A., Waldmann T., Wenz M., Eyll M., Geelvink M., Gereitzig M., Rüchel N., et al. EGFR activity addiction facilitates anti-ERBB based combination treatment of squamous bladder cancer. Oncogene. 2020;39:6856–6870. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01465-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

