Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fermented Lotus Root and Linoleic Acid in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Cells
- PMID: 33228085
- PMCID: PMC7699317
- DOI: 10.3390/life10110293
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fermented Lotus Root and Linoleic Acid in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Cells
Abstract
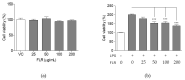
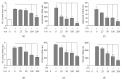
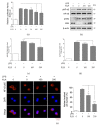
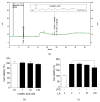
Inflammation is a protective response of the innate immune system. However, aberrant inflammatory responses lead to various diseases. Lotus root, the edible rhizome of Nelumbo nucifera, is a popular traditional herbal medicine in East Asia. In a previous study, we reported that fermented lotus root (FLR) alleviated ethanol/HCl-induced gastric ulcers in rats by modulating inflammation-related genes. However, the mechanisms underlying the anti-inflammatory effects of FLR and its major constituent, linoleic acid (LA), are still largely unknown. In this study, we investigated the anti-inflammatory effects of FLR and LA on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 murine macrophages. We found that FLR inhibited LPS-induced expression of inflammatory mediators through down-regulation of NF-κB activity. Similarly, LA also attenuated LPS-induced inflammatory responses and reduced LPS-induced phosphorylation of proteins associated with NF-κB signaling, such as ERK, JNK, and p38. Overall, our results suggested that FLR and LA may effectively ameliorate inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: MAPK; NF-κB; anti-inflammatory effect; fermented lotus root.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
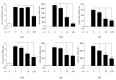
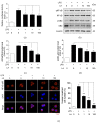
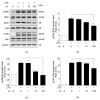
References
-
- De Lavor E.M., Fernandes A.W.C., de Andrade Teles R.B., Leal A., de Oliveira Junior R.G., Gama E.S.M., de Oliveira A.P., Silva J.C., de Moura Fontes Araujo M.T., Coutinho H.D.M., et al. Essential Oils and Their Major Compounds in the Treatment of Chronic Inflammation: A Review of Antioxidant Potential in Preclinical Studies and Molecular Mechanisms. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018;2018:6468593. doi: 10.1155/2018/6468593. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu S., Wu D., Sun G., Geng F., Shen Y., Tan J., Sun X., Luo Y. Gastroprotective effects of Kangfuxin against water-immersion and restraint stress-induced gastric ulcer in rats: Roles of antioxidation, anti-inflammation, and pro-survival. Pharm. Biol. 2019;57:770–777. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2019.1682620. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

