Innervation of the distal part of the vastus medialis muscle is endangered by splitting its muscle fibers during total knee replacement: an anatomical study using modified Sihler's technique
- PMID: 33228445
- PMCID: PMC8158273
- DOI: 10.1080/17453674.2020.1851459
Innervation of the distal part of the vastus medialis muscle is endangered by splitting its muscle fibers during total knee replacement: an anatomical study using modified Sihler's technique
Abstract
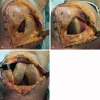
Background and purpose - The distal part of the vastus medialis muscle is an important stabilizer for the patella. Thus, knowledge of the intramuscular nerve course and branching pattern is important to estimate whether the muscle's innervation is at risk if splitting the muscle. We determined the intramuscular course of the nerve branches supplying the distal part of the vastus medialis muscle to identify the surgical approach that best preserves its innervation.Material and methods - 8 vastus medialis muscles from embalmed anatomic specimens underwent Sihler's procedure to make soft tissue translucent while staining the nerves to study their intramuscular course. After dissection under transillumination using magnification glasses all nerve branches were evaluated.Results - The terminal nerve branches were located in different layers of the muscle and ran mostly parallel but also transverse to the muscle fibers. In half of the cases, the latter formed 1 to 3 anastomoses and coursed close to the myotendinous junction. Additionally, most of the branches extended into the ventromedial part of the knee joint capsule.Interpretation - To preserve the innervation of the distal part of the vastus medialis muscle, any split of the muscle during surgical approaches to the knee joint should be avoided.
Figures



References
-
- Calguner E, Erdogan D, Elmas C, Bahcelioglu M, Gozil R, Ayhan M S.. Innervation of the rat anterior abdominal wall as shown by modified Sihler’s stain. Med Princ Pract 2006; 15(2): 98–101. - PubMed
-
- Clayton M L, Thirupathi R.. Patellar complications after total condylar arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Rel Res 1982; 170: 152–5. - PubMed
-
- Cooper R E Jr, Trinidad G, Buck W R.. Midvastus approach in total knee arthroplasty: a description and a cadaveric study determining the distance of the popliteal artery from the patellar margin of the incision. J Arthroplasty 1999; 14(4): 505–8. - PubMed
-
- Dalury D F, Jiranek W A.. A comparison of the midvastus and paramedian approaches for total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 1999; 14(1): 33–7. - PubMed
-
- Dalury D F, Snow R G, Adams M J.. Electromyographic evaluation of the midvastus approach. J Arthroplasty 2008; 23(1): 136–40. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
