Enriched environment ameliorates adult hippocampal neurogenesis deficits in Tcf4 haploinsufficient mice
- PMID: 33228529
- PMCID: PMC7684915
- DOI: 10.1186/s12868-020-00602-3
Enriched environment ameliorates adult hippocampal neurogenesis deficits in Tcf4 haploinsufficient mice
Abstract
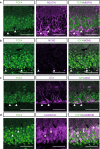
Background: Transcription factor 4 (TCF4) has been linked to human neurodevelopmental disorders such as intellectual disability, Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome (PTHS), autism, and schizophrenia. Recent work demonstrated that TCF4 participates in the control of a wide range of neurodevelopmental processes in mammalian nervous system development including neural precursor proliferation, timing of differentiation, migration, dendritogenesis and synapse formation. TCF4 is highly expressed in the adult hippocampal dentate gyrus - one of the few brain regions where neural stem / progenitor cells generate new functional neurons throughout life.
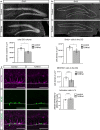
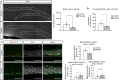
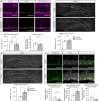
Results: We here investigated whether TCF4 haploinsufficiency, which in humans causes non-syndromic forms of intellectual disability and PTHS, affects adult hippocampal neurogenesis, a process that is essential for hippocampal plasticity in rodents and potentially in humans. Young adult Tcf4 heterozygote knockout mice showed a major reduction in the level of adult hippocampal neurogenesis, which was at least in part caused by lower stem/progenitor cell numbers and impaired maturation and survival of adult-generated neurons. Interestingly, housing in an enriched environment was sufficient to enhance maturation and survival of new neurons and to substantially augment neurogenesis levels in Tcf4 heterozygote knockout mice.
Conclusion: The present findings indicate that haploinsufficiency for the intellectual disability- and PTHS-linked transcription factor TCF4 not only affects embryonic neurodevelopment but impedes neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult mice. These findings suggest that TCF4 haploinsufficiency may have a negative impact on hippocampal function throughout adulthood by impeding hippocampal neurogenesis.
Keywords: Adult neurogenesis; Enriched environment; Hippocampus; Intellectual disability; PTHS; Tcf4.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Mary L, Piton A, Schaefer E, Mattioli F, Nourisson E, Feger C, et al. Disease-causing variants in TCF4 are a frequent cause of intellectual disability: lessons from large-scale sequencing approaches in diagnosis. Eur J Hum Genet. 2018;26(7):996–1006. doi: 10.1038/s41431-018-0096-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bedeschi MF, Marangi G, Calvello MR, Ricciardi S, Leone FPC, Baccarin M, et al. Impairment of different protein domains causes variable clinical presentation within Pitt-Hopkins syndrome and suggests intragenic molecular syndromology of TCF4. Eur J Med Genet. 2017;60(11):565–571. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2017.08.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

